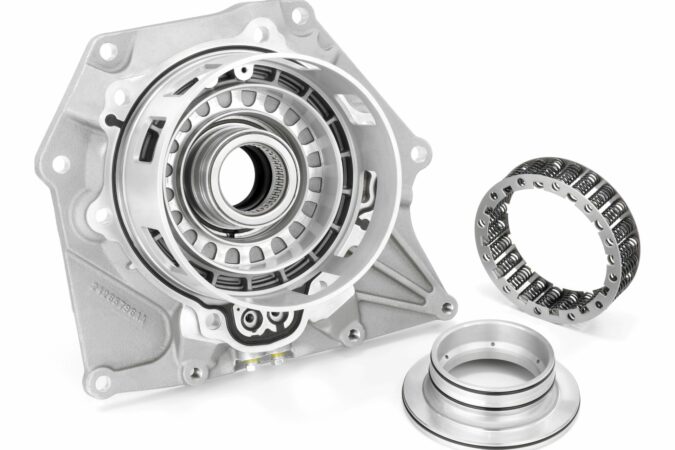
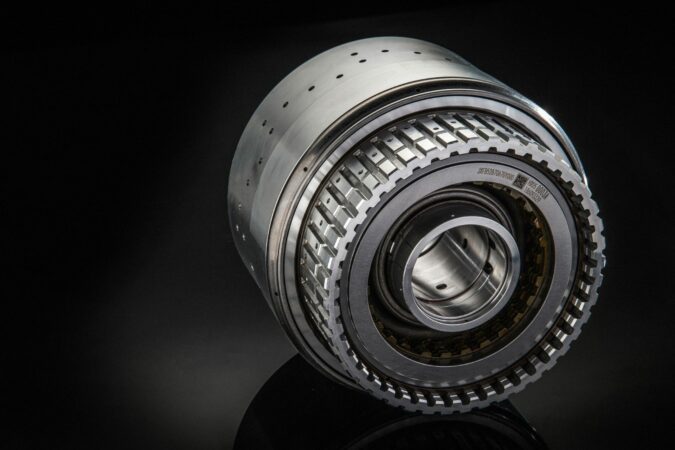
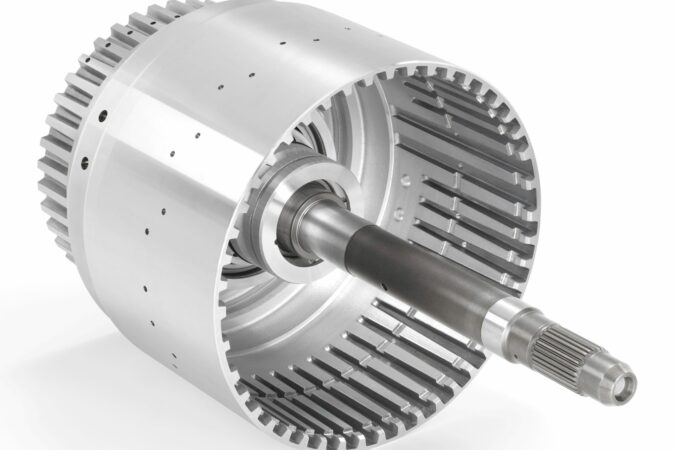
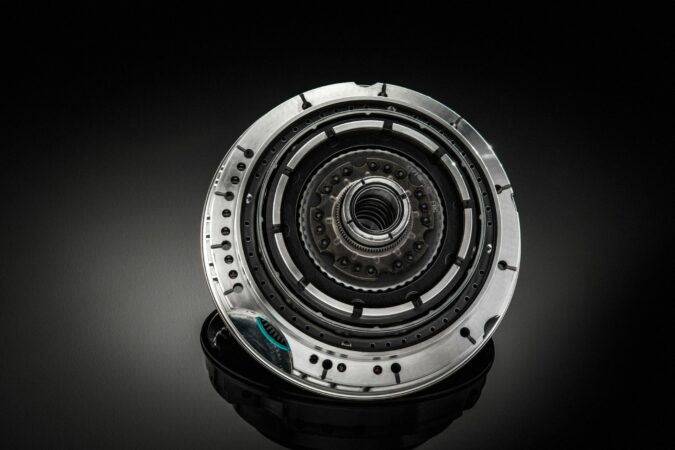
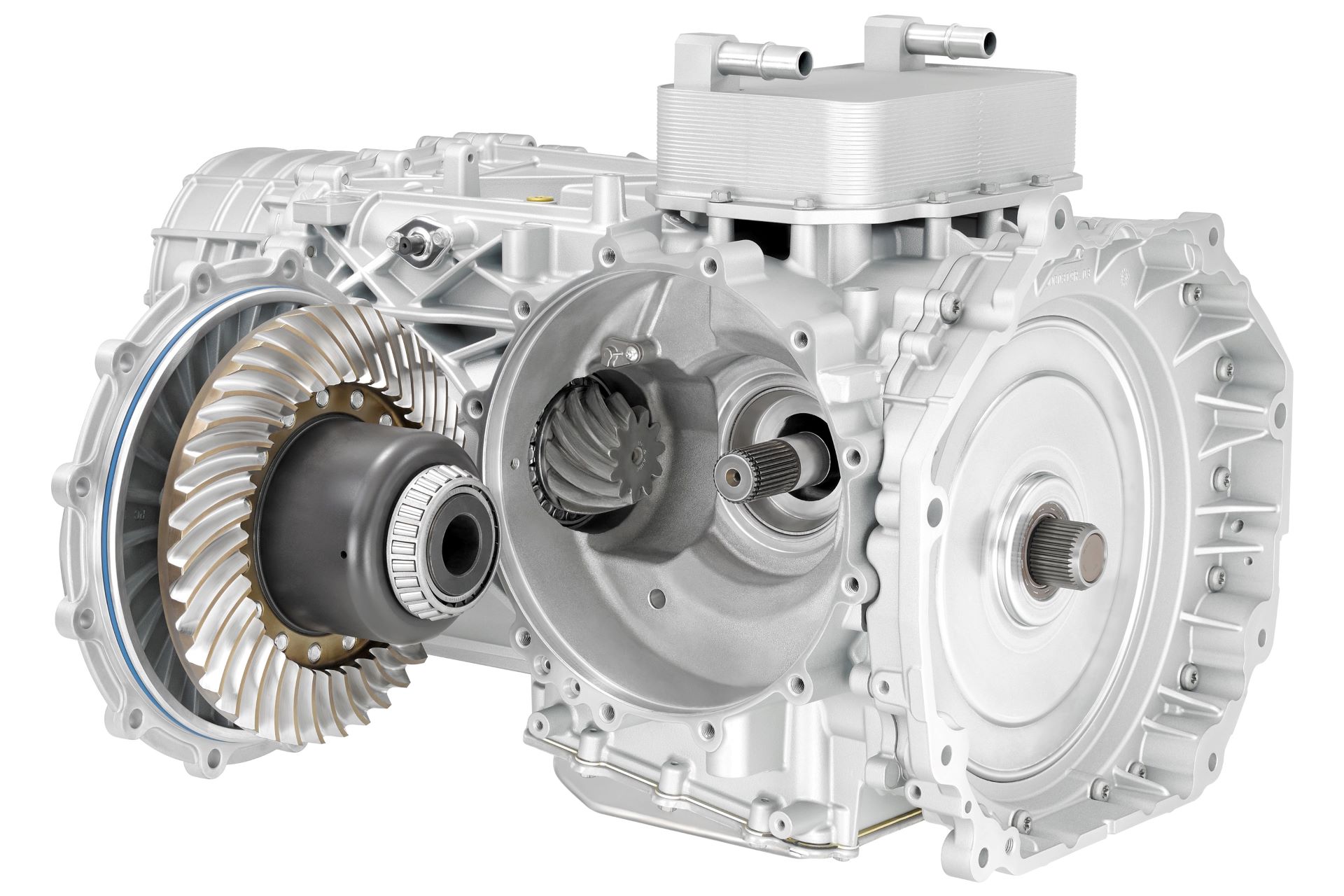
There’s a good probability that your throw out bearing is failing if you hear a loud noise when your car is in gear, and it’s not the engine. This part is in charge of disengaging the clutch pedal so that shifting gears is possible.
An essential part of the transmission, the throw-out bearing, sometimes referred to as the clutch release bearing, disengages the clutch when the clutch pedal is depressed. Vibrations, noise, and difficult shifting are indications of a faulty throwout bearing.
The throw out bearing replacement cost, spare parts, and labor price is between $200 and $450. We’ll talk about the signs of a bad throwout bearing in this blog post and how much it will cost to replace it.
- How a Throw Out Bearing works
- What Are the Signs Of a Bad Clutch?
- How To Inspect It?
- Reasons They Turn Bad?
- How To Replace It?
- When Should It Be Replaced?
- What Are The Symptoms?
- What Is the Replacement Cost?
Throw Out Bearing
A throwout bearing, often called a clutch release bearing, is a crucial part of the mechanism that releases the clutch in a normal car when the driver shifts gears to momentarily disconnect the engine from the manual transmission.
When the throw-out bearing clutch is in the engaged position, the throw-out bearing advances to the flywheel and presses the release levers of the pressure plate against the pressure plate spring. This procedure detaches the engine from the wheels to change the gears on the car.
The clutch release bearing returns to its initial position after the clutch pedal is released, re-connecting the engine’s power to the wheels via the transmission. In the clutch assembly of an automobile transmission, the throwout bearing is located between the clutch fork and the pressure plate fingers.
Signs Of A Bad Clutch
There are signs of a bad clutch that can alert you to the possibility that your throw-out bearing clutch is damaged or not operating properly.
1. Having To Increase RPMs
Most people who operate a manual transmission are familiar with their car. They have a general idea of how many RPMs are needed to achieve certain speeds in various gears. Your clutch disc may begin to slip as it begins to wear.
And if you need a better understanding of how RPMs work, do head over to our detailed explainers on what RPM should a car idle at, or if you have an issue where the RPM fluctuates while you’re accelerating, as well as problems where your car won’t accelerate but the RPMs go up.
For more insight, do check out our guide on the symptoms of a slipping clutch. When this occurs, you’ll discover it requires more RPMs than you anticipated to reach the desired speed. This is related to the grinding sound and burning odor.
2. It’s Hard To Shift Gears
The driver can smoothly change gears with a healthy clutch. Gear changes are challenging as the clutch begins to deteriorate. A harsher transition is used in place of the previous smooth gear shift. The clutch pedal might not work as it usually does, and shifting into gear might not be as effortless as it once was.
As such, this might be what causes issues where your car won’t go into gear, or if your car won’t move in drive. Elsewhere, it might cause other problems, such as how your manual transmission won’t engage any gear, if your transmission is shifting hard, or should your truck won’t move in any gear.
3. Burning Odor
If your throw-out bearing clutch disc begins to burn (i.e. the smell of a burned clutch), you might need to replace it. You can change gears by using the clutch disc, which is a friction plate that enables the transmission to function with the engine.
The friction covering on the clutch disc wears off over time, leaving the clutch disc exposed to the metal on metal as you shift gears. This not only causes injury but also has a burning smell. If you smell burning while driving, your transmission may be grinding.
4. Grinding Sounds During Gear Changes
You might hear a grinding noise when you shift gears while driving. The clutch disc or the transmission’s synchronizers may be to blame for this grinding sound. To improve shifting when changing between RPM ranges, synchronizers are used.
Whatever the cause, hearing a grinding noise when shifting or driving is a surefire indication that your car needs to be looked at by a mechanic.
5. A Soft Or Sagging Clutch Pedal
However, a spongy clutch pedal, unrelated to the clutch disc, indicates that your transmission needs to be serviced. Air in the system, issues with the clutch master cylinder, or a leak in the clutch fluid could be to blame for this.
Both will cause the throw-out bearing clutch pedal to feel mushy or spongy. The pedal may even occasionally fall to the ground and be unable to rise again. Besides diagnosing the throw out bearing, it’s also worth considering a clutch pedal adjustment.
6. Sluggish Acceleration
You should have your transmission evaluated if your engine is revving as soon as possible, but the car doesn’t seem to be accelerating properly. This could be an indication of a clutch problem.
How To Inspect Your Car’s Throwout Bearings
Take your car for a test drive and use a few easy tests to see whether the clutch release bearing is the issue. This is one of the finest ways to examine this component. As you use the clutch and shift gears on the road, pay close attention to what is being spoken.
First, listen for any unusual noises made with the clutch pedal fully depressed and the transmission in gear. Next, while the transmission is in first gear, pay attention as you let off the clutch.
When doing this, if you hear any strange noises, it’s likely that the throwout bearing or pilot bearing has to be replaced. Throwout bearing noise should be taken seriously as an early sign of failure.
How do you identify the failed bearing? While the clutch is fully engaged, put the transmission into neutral. If the noise persists, the throwout bearing is to blame. The pilot bearing has to be replaced if the noise has disappeared. When in doubt, have your mechanic make a professional analysis.
Throw Out Bearing Failure
1. Driving While Leaning Against The Clutch Pedal
This practice is referred to as “riding the clutch.” When not actively shifting, having your foot on the pedal might result in unnecessary damage to the release bearing by keeping it permanently engaged. When stopped or not actively shifting, letting your foot rest on the clutch pedal lessens wear on the bearing and other clutch components.
2. A High RPM Gear Change
You must know when to shift gears when operating a vehicle with a manual transmission. When shifting, the RPMs should be at a low level. Otherwise, the bearing operates under its maximum load and ages more quickly.
3. Normal Wear And Tear
Clutch-release bearings deteriorate with use, just like any other moving component. Every time you drive, friction gradually wears away components that alter the bearing’s size and finish.
If the release bearing isn’t changed, the fit and finish will no longer fit into the assembly correctly, leading to the clutch failing.
4. Deficiency In Pressure Plate Alignment
A little unequal pressure load may result from improper pressure plate alignment with the release bearing. As a result, the uneven wear will result in an inappropriate component fit and perhaps expedite bearing failure.
Throw Out Bearing Replacement
A few simple tools will suffice to perform the relatively straightforward process of replacing the throwout bearing.
- Remove the battery’s connector.
- Take the driveshaft out. This will provide you with extra workspace and guard against driveshaft damage while you’re working.
- The bell housing and slave cylinder should be disconnected.
- Bell housing removal from the engine requires removing the bell housing bolts.
- From the bell housing, remove the old throw-out bearing.
- Remove any dirt or debris from the bell housing surface where the new throwout bearing will mate.
- Place the replacement throwout bearing within the bell housing.
- Tighten the nuts after reinstalling the bell housing on the engine.
- Reconnect the bell housing and the slave cylinder.
- Install the driveshaft again.
- Replug the batteries in.
- Check for leaks after starting the engine.
- To check sure the clutch is operating properly, test drives the car.
A throwout bearing replacement is a reasonably easy task that can be finished in an hour or two with a simple Blue Point tools kit. It is preferable to leave this task to a trained expert if you are unsure of your abilities to finish it.
When Should A Throw Out Bearing Be Replaced
If you have all the required equipment and components, replacing a throwout bearing shouldn’t take more than a couple of hours. The process’s longest step is taking the transmission out of the way so you can access the clutch assembly.
The old throwout bearing can be taken out and replaced with the new one once the transmission has been removed. Before you can use your automobile again, you must reinstall the transmission and bleed the clutch system.
Let a qualified mechanic handle the work if you have never replaced a throwout bearing is usually advisable. They will have the skills and knowledge necessary to complete the task promptly and effectively.
Bad Throw Out Bearing Symptoms
Throw-out bearing noise when depressing the clutch is the most typical symptom. If the bearing is damaged, you may experience vibrations when depressing the clutch pedal. When changing gears, you can hear grinding or have other issues.
Below, we’ve highlighted a more thorough list of bad throw-out-bearing symptoms to watch out for:
1. Noise Whenever The Clutch Is Depressed
When you depress the clutch, your throwout bearing presses up against the pressure plates, and if the fit isn’t constant and flush, it will create a lot of throw-out bearing noise.
Additionally, it won’t happen just once; the chatter will likely continue as long as the clutch is depressed, and those noises will only get louder as you actively press and release the clutch.
2. Vibrations In The Clutch Pedal
If your throwout bearing is damaged, you won’t just hear all that chattering; you’ll also feel it in the clutch. The throwout bearing rubs against the pressure plates as the clutch is depressed, causing the clutch to vibrate.
The vibrations will be more severe the worse the issue is. However, you might not notice the vibrations right away if the issue is only getting started.
3. Gear-Changing Issues
One of the essential parts of your car’s clutch, whose sole function is to assist you in shifting gears, is the throwout bearing. Therefore, it is not unusual that you would experience shifting issues if your throwout bearing starts to malfunction.
Typically, this issue doesn’t surface until the issue has lingered for a while. It’s also when the issue becomes more dangerous because you’ll find it difficult to change gears while driving, which is a surefire way to cause an accident.
4. An Overly Stiff Clutch
It won’t press against the clutch pressure plates as easily as it should if your throwout bearing is causing a lot of issues. Even though it might not seem like a significant deal, you will need to apply more force to the clutch pedal to fully depress it.
This additional force will probably be insignificant at first, but as the issue worsens, it will become more significant. Additionally, it’s possible for the throwout bearing to “catch,” which would cause your clutch pedal to momentarily become stuck. This could cause serious issues when you’re driving.
5. Grinding While Changing Gears
Anyone who has ever operated a stick shift car (and understands how to drive manual and how to drive a manual) knows the sound of grinding gears. The throwout bearing, however, may be to blame if you’re following all the right procedures and have the clutch pedal firmly depressed, but you’re still hearing grinding sounds.
It can make your clutch re-engage as it chatters or keep it from disengaging all the way in the first place. You’ll notice the issue as loud and evident grinding occurs when you try to shift gears. You might be able to ignore this issue for a short while, but doing so will only invite bigger problems in the future.
Throw Out Bearing Replacement Cost
The throw out bearing replacement cost averages between $400 and $1500, with labor accounting for most of that sum. This is because an aftermarket throwout bearing normally costs only $10 to $30. A throwout bearing may be inexpensive, but getting to one can be difficult.
One of the more challenging tasks to complete on your own is the removal of the entire transmission. Furthermore, due to the extra mechanic labor rate, most individuals don’t just replace the clutch bearing. Instead, they often replace the clutch as a whole, saving them from paying twice quickly for labor.
The price for a qualified mechanic to replace the clutch in your car is between $1,200 and $1,500. Even while that costs substantially more than merely replacing the throwout bearing, your clutch won’t be far behind if you require a new throwout bearing.
If the task is ultimately required twice, you will incur additional costs of $600 that might have been avoided if it were completed all at once.
Throw Out Bearing Grease
For starters, take note that the majority of sealed bearings are pre-greased with a 25%–35% grease fill at the manufacturing. The relubrication period is longer than the anticipated life of the bearing, so this is the only grease the bearings will ever require.
It may be tempting to lubricate the bearings every day or to keep pumping until grease escapes the seals. However, this virtually eliminates the seal’s capacity to keep impurities out of the grease, and an excessive amount of grease “churns” inside the bearing, creating resistance and causing a rapid buildup of heat.
[(OD in inches) x (width in inches) x 0.14″] yields the weight in ounces. [(OD in mm) x (width in mm) x 0.005] to calculate grams. A 6209 ball bearings car, for instance, might be used in your application and run continuously at 1,750 RPM in a spotless machine for seven days a week. A 6209 bearing has a 19mm width, an OD of 85mm, and a shaft diameter of 45mm.
According to the chart and calculation, only 8 grams of grease are required for the bearing every 10,000 hours. If your grease gun produces 1.35 grams of grease per stroke, a bearing will require 6 strokes every 13 months, or you may average it out to about 1 stroke every 8 weeks.
When lubricating a bearing with a zerk, ensure that both the zerk and the grease gun nozzle are clean and that the zerk is always covered between greasings. If not, you risk spewing pollutants and dirt directly into your bearings.
Pilot Bearing vs Throw Out Bearing
The clutch release bearing makes a connection between the throw out bearing fork and the pressure plate fingers. The pressure plate is moved away from the flywheel when the clutch pedal is depressed, allowing the clutch plate to revolve between them freely.
The fork presses on the release bearing, which presses the fingers. The transmission input shaft’s front end is held in place in the middle of the flywheel by the pilot bearing, which is frequently a bushing rather than a bearing. It serves as an alignment tool.
FAQs On Throw Out Bearing
What Is A Throw Out Bearing
During a gear shift, the throwout bearing momentarily disengages the car’s engine from the transmission. The throwout bearing and flywheel are brought closer together once the clutch pedal is depressed. The pressure plates release fingers are pushed inward due to this movement.
How To Tell If A Clutch Is Bad
One of the first symptoms you could experience is a soft or spongy feeling when you press down on your clutch. Keep an eye out for how your clutch feels when you are driving. Knowing how it typically feels will help you recognize problems when they arise. Your clutch may be failing if you notice that your car is difficult to shift and doesn’t engage smoothly. You’ll have the highest chance of seeing this when you move into reverse and first gear.
How Does A Bearing Work
By providing smooth inner and exterior surfaces for the balls to roll against and smooth balls or rollers, bearings reduce friction. These balls or rollers transport the weight so that the apparatus may spin smoothly.
What Does A Bad Bearing Sound Like
A faulty wheel bearing typically makes a cyclical chirping, squealing, or growling noise. If the sound fluctuates proportionally to the speed of the vehicle, this is another sign that the wheel bearings cause it. At any given moment, the sound could suddenly stop or it could get progressively worse.
What Does A Bad Flywheel Look Like
Because it might stop the engine from turning over, a damaged flywheel can contribute to starting issues. This frequently results from a seized flywheel, which won’t turn even when the engine is started. The starting motor may experience issues as well. Your automobile may smell like burning due to a damaged flywheel. The flywheel is a component of the engine that contributes to the car’s power. If it malfunctions, the engine may overheat and smell like burned rubber.
What Happens When Throwout Bearing Fails In A Manual Transmission
The defective throwout bearing can make your car’s clutch pedal feel stiff when pressing it down as the problem worsens. Any driver should consider this a warning sign and take immediate action.
How Long Can You Drive With A Bad Throw Out Bearing
Most throwout bearings are durable for the entire clutch life. On average, clutches last 60,000 miles. Depending on driving patterns, vehicle type, and temperature, they can live much longer or fail much sooner.
Is The Clutch Part Of The Transmission
The clutch is a component of a manual transmission that is sometimes overlooked. The mechanical component known as a clutch is what moves all of the vehicle’s power from the engine to the transmission. It would be quite challenging to shift gears and transfer power without a properly functioning clutch.
How To Fix Throwout Bearing Noise
Changing how you engage the clutch pedal in your car is one of the simplest ways to delay throwout bearing wear. It is advisable to only engage the clutch for as little time as possible; in other words, when you stop, put your automobile in neutral rather than keeping your foot firmly planted on the clutch.
What Does A Bad Throwout Bearing Sound Like
If the throwout bearing is damaged, it’s common for drivers to hear a grinding or rattling sound when depressing the clutch pedal. Although these noises are alarming, a differential diagnosis is necessary because they could also be symptoms of problems with your clutch or transmission.
How Does A Throwout Bearing Work
The throwout bearing advances to the flywheel when the clutch is engaged and presses the release levers of the pressure plate against the pressure plate spring there. By doing this, the engine is decoupled from the wheels, allowing the car to change gears. The clutch release bearing returns to its initial position after the clutch pedal is released, re-connecting the engine’s power to the wheels via the transmission.
How Much To Replace Throw Out Bearing
Whether you DIY it or take it to the technician, the typical cost to repair a throwout bearing ranges from $30 to $820. Taxes, fees, and the specific make, model, or location of your car are not taken into account in the price range provided, which is based on the national average for all vehicles.
What Causes A Throwout Bearing To Go Bad
Every time you drive, friction gradually wears away components that alter the bearing’s size and finish. If the release bearing isn’t changed, ultimately, the fit and finish will no longer fit into the assembly correctly, leading to the clutch failing.
How Long Will A Noisy Clutch Release Bearing Last
There isn’t a conclusive response to this. You could get an hour or up to five years out of a noisy throwout bearing. Everything relies on the precise type of bearing wear or damage, bearing quality, and driving style. The best course of action is to service and replace your throwout bearing as soon as you feel it is loud.
What Happens When A Throw Out Bearing Fails
When applying the clutch pedal, a whirring or growling sound that disappears when the pedal is released is a common sign of a worn throwout bearing. When there is insufficient clutch play, the throwout bearing can prematurely wear out since it will continue to spin.
Throw Out Bearing: Final Verdict
After reading this article, you know the indicators of a bad throw-out bearing that are simple to spot. Please seek the advice of a qualified auto mechanic to address any other indicators you may see in your car so that they may be fixed before it becomes worse.
The answer to the question, “How long can you drive with a defective throwout bearing?” can be deduced from the information on this page. In most circumstances, you can drive for a long period with a faulty throwout bearing, but occasionally you might only be able to do so for a short while.
Nevertheless, the throwout bearing and other parts of your car should be kept in great functioning order.