- What Is a Catalytic Converter
- Installing a Catalytic Converter
- Problems with Catalytic Converters
- Different Types of Catalytic Converters
- Faulty or Missing Catalytic Converter
- How to Tell If You Need a New One
- Cost of a Faulty Catalytic Converter
- What Are the Environmental Benefits
- Tips for Maintaining Your Exhaust System
- Exploring Alternative Solutions
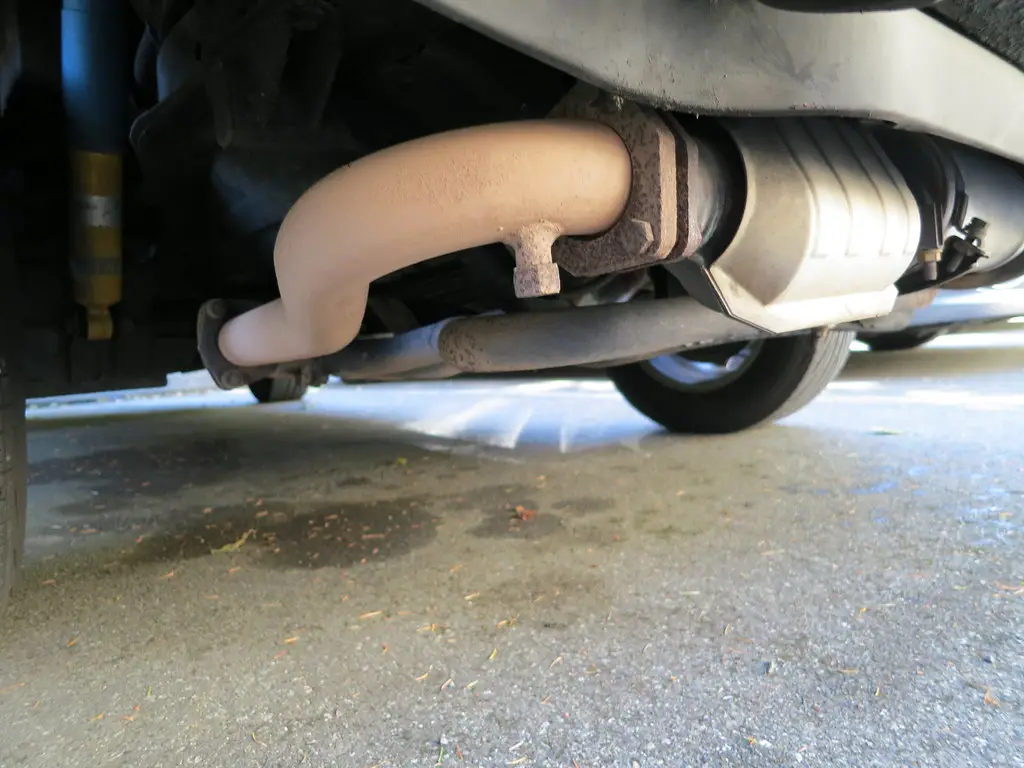
What Is a Catalytic Converter and How Does It Work?
A catalytic converter is an emissions control device that is fitted to the exhaust system of a vehicle. It works by converting harmful pollutants in the exhaust gases into less harmful substances before they are released into the atmosphere.
The catalytic converter does this by using a catalyst, usually platinum or palladium, to chemically convert pollutants such as carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons into carbon dioxide and water vapor.
For more insight into what goes inside a catalytic converter, check out our guides on which catalytic converters have the most rhodium, as well as how much platinum is in a catalytic converter. The catalytic converter works by passing the exhaust gases through a honeycomb-like structure coated with the catalyst material.
As the exhaust passes through this structure, it comes into contact with the catalyst which causes chemical reactions to take place that convert harmful pollutants into less harmful substances. This process helps reduce air pollution from vehicle emissions and makes vehicles more environmentally friendly.
Catalytic converters are required on all modern vehicles to meet emission standards set by governments around the world. Without them, vehicles would produce much higher levels of air pollution than they do today, leading to increased health risks for people living near busy roads or highways where traffic is heavy.
The Benefits of Installing a Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter is an important component of a vehicle’s exhaust system. It helps to reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere by converting them into less harmful substances. Installing a catalytic converter can provide numerous benefits, both for the environment and for your vehicle.
- One of the primary benefits of installing a catalytic converter is that it helps to reduce air pollution. The device works by converting toxic gases such as carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons into less harmful substances like nitrogen and water vapor. This reduces the amount of these pollutants released into the atmosphere, helping to improve air quality in your area.
- Another benefit of installing a catalytic converter is that it can help improve fuel efficiency in your vehicle. The device works by reducing emissions from your engine, which allows it to run more efficiently and use less fuel in the process. This can result in significant savings on fuel costs over time, making it an economical choice for many drivers.
- Finally, installing a catalytic converter can also help extend the life of your vehicle’s engine components by reducing wear and tear caused by excessive emissions from its exhaust system. By reducing these emissions, you can help ensure that all parts are functioning properly and last longer than they would otherwise without this device installed on your car or truck’s exhaust system.
Overall, there are numerous benefits associated with installing a catalytic converter on your vehicle’s exhaust system including improved air quality, increased fuel efficiency, and extended engine life expectancy due to reduced wear-and-tear caused by excessive emissions from its exhaust system components.
Therefore, if you are looking for ways to make sure that you get the maximum performance out of your car or truck (especially with a high-flow catalytic converter or a high-flow catalytic converter from Magnaflow) while also helping protect our environment, then investing in this type of device may be worth considering.
Common Problems with Catalytic Converters and How to Fix Them
The catalytic converter is an important part of a vehicle’s exhaust system. It helps to reduce the number of harmful emissions released into the atmosphere. Unfortunately, catalytic converters can sometimes malfunction, leading to a variety of problems. Here are some common issues and how to fix them.
- One common problem with catalytic converters is clogging due to the buildup of carbon deposits or other debris in the exhaust system. This can cause reduced engine performance and increased fuel consumption as well as increased emissions levels. To fix this issue, it is necessary to clean out the exhaust system and replace any damaged parts such as oxygen sensors or spark plugs that may be contributing to the problem. So, be wary of the symptoms of a clogged catalytic converter and the signs of a bad catalytic converter.
- Another issue that can occur with catalytic converters is overheating due to a lack of airflow through the converter itself or from an obstruction in the exhaust pipe downstream from it. This can cause damage to both the converter and other components in your vehicle’s exhaust system, so it’s important to address this issue quickly by removing any obstructions or replacing any damaged parts such as mufflers or resonators that may be causing restricted airflow through your vehicle’s exhaust system.
- Finally, another common problem with catalytic converters is corrosion caused by exposure to moisture over time which can lead to cracks in its housing and eventual failure of its internal components. To prevent this from happening, it’s important for drivers regularly inspect their vehicles for signs of corrosion on their catalytic converters and replace them if necessary before they become too damaged for repair.
In conclusion, there are several common problems associated with catalytic converters that drivers should be aware of to keep their vehicles running smoothly while also reducing emissions levels released into our environment. By following these tips on how best to address these issues when they arise, you will help ensure your vehicle remains safe and reliable for years to come.
Understanding the Different Types of Catalytic Converters
Catalytic converters are an important part of a vehicle’s exhaust system, as they help reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere. There are several different types of catalytic converters available, each designed to meet specific needs and requirements.
Understanding the differences between these types can help you make an informed decision when selecting a converter for your vehicle.
- The most common type of catalytic converter is the three-way converter, which is designed to reduce emissions from gasoline engines. This type of converter uses a combination of platinum, palladium, and rhodium to convert carbon monoxide (CO) into carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrocarbons (HC) into water vapor (H2O), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into nitrogen gas (N2). Three-way converters are typically found on newer vehicles that use gasoline engines.
- Another type of catalytic converter is the two-way converter, which is designed for diesel engines. This type uses only platinum and palladium to convert CO into CO2 and HCs into H2O. Two-way converters are typically found on older diesel vehicles that do not have advanced emission control systems in place.
- Finally, there are oxidation catalysts that can be used with both gasoline and diesel engines to reduce HC emissions by up to 90%. These types use precious metals such as platinum or palladium along with other materials such as aluminum oxide or zeolite to oxidize HCs before they enter the atmosphere. Oxidation catalysts can be used in conjunction with other emission control systems such as particulate filters or selective catalyst reduction systems to further reduce emissions from vehicles equipped with either gasoline or diesel engines.
By understanding the different types of catalytic converters available today, you can make an informed decision when selecting one for your vehicle’s exhaust system needs.
The Impact of a Faulty or Missing Catalytic Converter on Your Vehicle’s Performance
A catalytic converter is an important component of a vehicle’s exhaust system. It helps to reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere by converting them into less harmful substances. When a catalytic converter is faulty or missing, it can have a significant impact on your vehicle’s performance.
- The most obvious effect of a faulty or missing catalytic converter is decreased fuel efficiency. Without the catalyst, more fuel will be burned to produce the same amount of power, resulting in lower gas mileage and increased emissions. Additionally, without the catalyst present to convert pollutants into less harmful substances, more pollutants will be released into the atmosphere from your vehicle’s exhaust system. This can lead to air pollution and health problems for those living near busy roads or highways where vehicles with faulty converters are common.
- Another issue that may arise from having a faulty or missing catalytic converter is engine misfires and stalling due to an increase in unburned hydrocarbons entering the combustion chamber from incomplete combustion caused by insufficient oxygen levels in the exhaust stream due to lack of conversion by the catalyst. This can cause damage to other components such as spark plugs and oxygen sensors which could lead to further issues with your vehicle’s performance if not addressed promptly.
- Finally, having a faulty or missing catalytic converter may also result in increased noise levels coming from your vehicle’s exhaust system due to an increase in backpressure caused by the incomplete conversion of pollutants within it which can be both annoying and potentially dangerous when driving at high speeds on highways or other busy roads where sound levels must remain low for safety reasons.
In conclusion, having a faulty or missing catalytic converter can have serious implications for both you and your vehicle’s performance as well as for those living near busy roads where vehicles with these issues are common due its effects on fuel efficiency, emissions output, engine misfires/stalling and increased noise levels coming from its exhaust system.
How to Tell If Your Car Needs a New Catalytic Converter
“Catalytic Converter” by Hiddenpower is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 2.0
If your car is exhibiting any of the following symptoms, it may be time to consider replacing the catalytic converter:
1. Reduced engine performance – If you notice a decrease in power or acceleration, this could be an indication that your catalytic converter is not functioning properly.
2. Check engine light – A malfunctioning catalytic converter can trigger a “check engine” light on your dashboard. If this happens, it’s important to have the issue diagnosed and repaired as soon as possible.
3. Unusual smells – If you smell sulfur or rotten eggs coming from your exhaust pipe, this could indicate that there is an issue with the catalytic converter, and should be checked out by a professional mechanic immediately.
4. Increased fuel consumption – A faulty catalytic converter can cause increased fuel consumption due to reduced efficiency in converting pollutants into harmless gases before they are released into the atmosphere. This can lead to higher fuel costs over time if left unchecked and unrepaired for too long.
5. Rattling noises – If you hear rattling noises coming from underneath your car when accelerating, this could mean that pieces of the catalyst material inside of the converter have broken off and are now loose inside of it causing damage to other components within its system such as oxygen sensors or spark plugs which will need replacing if left unchecked for too long.
The Cost of Replacing a Faulty or Missing Catalytic Converter
The cost of replacing a faulty or missing catalytic converter can vary greatly depending on the make and model of your vehicle. Generally, the cost of a new catalytic converter ranges from $200 to $2,000. The price is largely determined by the type of car you drive and the complexity of installation.
In addition to purchasing a new catalytic converter, there may be additional costs associated with its replacement. These include labor costs for removal and installation, as well as any necessary parts such as gaskets or hangers that may need to be replaced during installation. Depending on your vehicle’s make and model, these additional costs can range from $50 to $500 or more.
It is important to note that some states have laws requiring vehicles with faulty or missing catalytic converters to pass an emissions test before they can be registered or driven legally on public roads. If your vehicle fails an emissions test due to a faulty or missing catalytic converter, you may also need to pay for repairs for it to pass inspection before it can be registered again.
Replacing a faulty or missing catalytic converter is not only expensive but also time-consuming; therefore it is important that you take steps now to maintain your vehicle’s emission system so that costly repairs are not needed in the future.
Regular maintenance such as changing the oil regularly and checking spark plugs will help ensure that your car runs efficiently and meets all applicable emission standards set by law enforcement agencies in your area.
What Are the Environmental Benefits of Using a Catalytic Converter?
A catalytic converter is an important component of a vehicle’s exhaust system, designed to reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere. By converting toxic gases such as carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons into less harmful substances, catalytic converters play a vital role in reducing air pollution.
The environmental benefits of using a catalytic converter are numerous. Firstly, they help to reduce emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx), which are known to cause smog and acid rain. Secondly, they also reduce emissions of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which can contribute to ground-level ozone formation and respiratory problems in humans.
Finally, they help to reduce the amount of carbon monoxide released into the atmosphere by up to 95%, making them an effective tool for improving air quality. In addition, catalytic converters can also improve fuel efficiency by allowing engines to run more efficiently at lower temperatures.
This helps conserve energy and reduces fuel consumption over time – leading to fewer greenhouse gas emissions from vehicles on the road. Overall, it is clear that using a catalytic converter has many environmental benefits – from reducing air pollution levels and improving air quality, right through to conserving energy and reducing greenhouse gas emissions from vehicles on our roads today.
Maintaining Your Car’s Exhaust System and Its Components, Including the Catalytic Converter
1. Regularly inspect your car’s exhaust system for any signs of damage or wear and tear. Look for any holes, cracks, rust, or other visible signs of damage that could lead to a leak in the system.
2. Make sure to replace any worn-out parts as soon as possible to avoid further damage and costly repairs down the line. Pay special attention to the catalytic converter, which is an important component of your car’s exhaust system that helps reduce emissions from your vehicle.
3. Check all hoses and clamps regularly for tightness and proper fitment on the exhaust components they are connected to. Loose hoses can cause leaks in the system which can lead to decreased performance and increased emissions from your vehicle.
4. Have a professional mechanic check your car’s oxygen sensors periodically as they are responsible for monitoring air-fuel ratios to ensure optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency levels are maintained at all times while driving your vehicle.
5. Make sure you use only high-quality fuel when filling up at the pump as low-quality fuel can cause build-up inside of the catalytic converter over time leading to it becoming clogged or damaged beyond repair.
6. Have a professional mechanic perform regular maintenance on your car’s exhaust system including checking spark plugs, wires, filters, and other components related to its operation. This will help ensure that everything is running smoothly so you don’t have any unexpected issues while driving down the road.
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Replacing an Old or Damaged Catalyst Converter
The catalyst converter is an essential component of a vehicle’s exhaust system, as it helps to reduce the number of harmful emissions released into the atmosphere. Unfortunately, due to its location and exposure to extreme temperatures, the catalyst converter can become damaged or worn out over time.
Replacing a damaged or old catalyst converter can be expensive and time-consuming, so many car owners are looking for alternative solutions.
- One option is to install a bypass pipe in place of the old converter. This involves removing the existing converter and replacing it with a straight pipe that allows exhaust gases to pass through without being filtered or treated. While this solution may be cheaper than replacing the entire converter, it should only be used as a temporary measure since bypassing emissions control systems is illegal in most states and countries.
- Another option is to install an aftermarket catalytic converter that meets current emission standards. These converters are designed specifically for older vehicles and can help reduce emissions while still providing adequate performance levels. However, they may not last as long as factory-installed converters due to their lower-quality materials and construction methods.
- Finally, some car owners opt for an oxidation catalytic converter (OCC). This type of device uses oxygen from outside air instead of relying on chemical reactions within the exhaust system itself; this makes them more efficient at reducing pollutants while also being more cost effective than traditional converters. However, OCCs require regular maintenance to keep them functioning properly over time; if not maintained properly they may become clogged with debris or fail prematurely due to corrosion or other damage caused by heat exposure from engine components nearby.
In conclusion, there are several alternatives available when it comes time to replace an old or damaged catalyst converter on your vehicle; however, each has its own advantages and disadvantages that must be weighed carefully before making any decisions about which solution will work best for you and your vehicle’s needs.


