- How Does a Catalytic Converter Work?
- Benefits of Having a Catalytic Converter
- Common Problems with Catalytic Converters
- How to Tell if You Have a Catalytic Converter
- Cost of Replacing a Catalytic Converter
- Different Types of Catalytic Converters
- Removing or Replacing a Catalytic Converter
- What Are the Environmental Benefits
- Is It Legal to Drive Without a Working One
- Maintaining the Life of Your Catalytic Converter
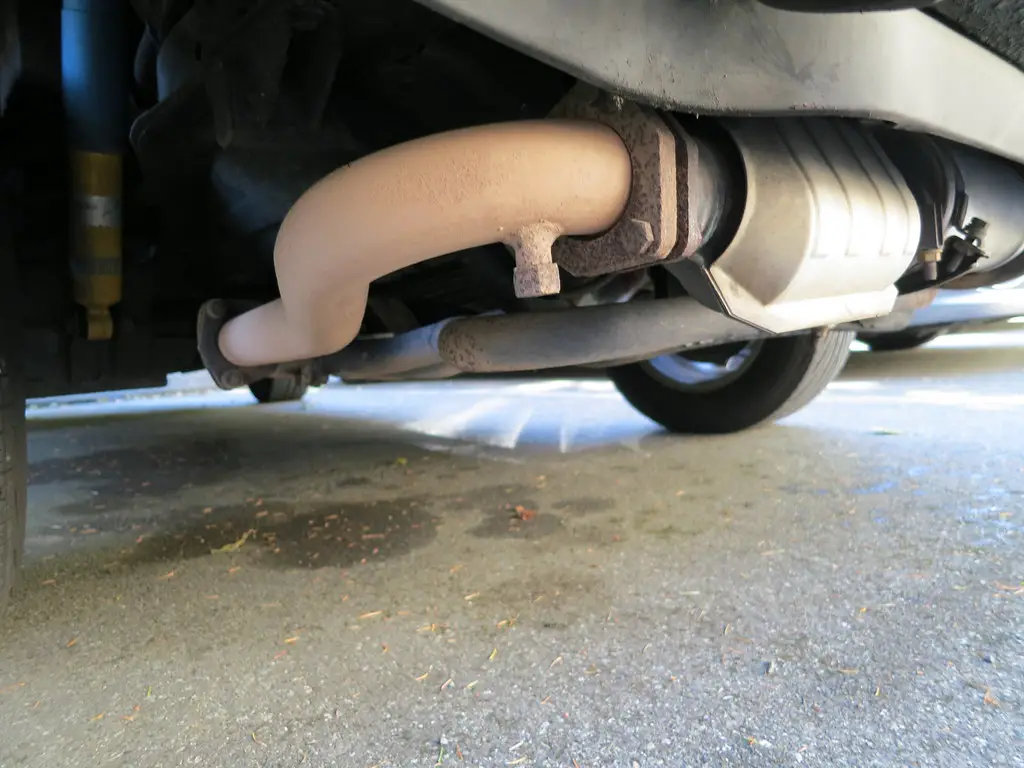
What is a Catalytic Converter and How Does it Work?
So, does my car have a catalytic converter? A catalytic converter is an emissions control device that is fitted to the exhaust system of a vehicle. It works by converting harmful pollutants in the exhaust gases into less harmful substances before they are released into the atmosphere.
The catalytic converter does this by using a catalyst, usually platinum or palladium, to chemically convert the pollutants into carbon dioxide and water vapor. The catalytic converter works by passing exhaust gases through a honeycomb-like structure coated with precious metals such as platinum and palladium.
These metals act as a catalyst, which means they speed up chemical reactions without being consumed themselves. To find out more about precious metals, check out our guide on which catalytic converters have the most rhodium, as well as how much platinum is in a catalytic converter.
As the exhaust gases pass through this structure, they come into contact with these metals and undergo chemical reactions that convert them from harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and hydrocarbons (HC) into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O). This process helps reduce air pollution caused by vehicle emissions.
In addition to reducing air pollution, catalytic converters also help improve fuel efficiency by allowing engines to run more efficiently at lower temperatures. You can confirm this by running a catalytic converter temperature test.
This is because when an engine runs at higher temperatures it produces more NOx which can be damaging to both human health and the environment if not properly controlled. By controlling these emissions with a catalytic converter, engines can run more efficiently while still producing fewer pollutants than before.
The Benefits of Having a Catalytic Converter in Your Car
The catalytic converter is an important component of a vehicle’s exhaust system. It helps to reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere by converting them into less toxic substances. This device has been mandatory in all cars since 1975, and its benefits are numerous.
First and foremost, a catalytic converter helps to reduce air pollution. By converting carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides into harmless gases such as carbon dioxide and water vapor, it reduces the amount of these pollutants that are released into the environment. This can help improve air quality in cities where smog levels are high due to vehicle emissions.
In addition to reducing air pollution, a catalytic converter also improves fuel efficiency by allowing engines to run more efficiently. By reducing emissions from vehicles, it allows engines to burn fuel more completely which results in better fuel economy and fewer trips to the gas station for refills.
Finally, having a catalytic converter installed on your car can help you save money on repairs down the road as well as increase its resale value when you decide it’s time for an upgrade or replacement vehicle.
Without this device installed on your car’s exhaust system, you may be subjecting yourself to costly repairs due to damage caused by excessive emissions or poor engine performance caused by inefficient burning of fuel due to a lack of proper filtration systems like those provided by the catalytic converter.
Additionally, having this device installed will make your car more attractive when selling or trading it in for another model since buyers know they won’t have additional costs associated with installing one themselves later down the line if they don’t already have one installed on their current vehicle’s exhaust system.
Overall, having a catalytic converter installed on your car is beneficial both environmentally and financially. Not only does it help reduce air pollution, but also improves fuel efficiency while saving you money on future repairs. Furthermore, having this device installed will make your car more attractive when selling or trading it in for another model.
Common Problems with Catalytic Converters and How to Fix Them
The catalytic converter is an important part of a vehicle’s exhaust system. It helps to reduce the number of harmful emissions released into the atmosphere. Unfortunately, catalytic converters can sometimes malfunction, leading to a variety of problems. Here are some common issues and how to fix them.
- One common problem with catalytic converters is clogging due to the buildup of carbon deposits or other debris in the exhaust system. This can cause reduced engine performance and increased fuel consumption as well as increased emissions levels. To fix this issue, it is necessary to clean out the exhaust system and replace any damaged parts such as oxygen sensors or spark plugs that may be contributing to the problem. So, be wary of the symptoms of a clogged catalytic converter, as well as whether can a bad catalytic converter cause a misfire.
- Another issue that can occur with catalytic converters is overheating due to a lack of airflow through the converter itself or from an obstruction in the exhaust pipe downstream from it. This can cause damage to both the converter and other components in your vehicle’s exhaust system, so it’s important to address this issue quickly by removing any obstructions or replacing any damaged parts such as mufflers or resonators that may be causing restricted airflow through your vehicle’s exhaust system.
- Finally, another common problem with catalytic converters is corrosion caused by exposure to moisture over time which can lead to cracks in its housing and eventual failure of its internal components. To prevent this from happening, it’s important for drivers regularly inspect their vehicles for signs of corrosion on their catalytic converters and replace them if necessary before they become too damaged for repair.
In conclusion, there are several common problems associated with catalytic converters that drivers should be aware of to keep their vehicles running smoothly while also reducing emissions levels released into our environment. By following these tips on how best to address these issues when they arise, you will help ensure your vehicle remains safe and reliable for years to come.
How to Tell if Your Car Has a Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter is an important part of a vehicle’s emissions system. It helps reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere by converting them into less harmful substances. If your car has a catalytic converter, it is important to make sure it is functioning properly to keep your vehicle running efficiently and safely.
Here are some ways to tell if your car has a catalytic converter (and the signs of a bad catalytic converter):
1. Check for an OBD-II port: Most cars manufactured after 1996 have an On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) port located under the dashboard near the steering wheel. This port can be used to connect a diagnostic tool that will tell you if your car has a catalytic converter or not.
2. Look for exhaust pipes: A catalytic converter is usually located between the engine and muffler, so look for two exhaust pipes coming from the engine instead of one if you suspect that your car may have one installed.
3. Listen for rattling noises: If there is something wrong with your catalytic converter, such as it being clogged or damaged (in addition to any damage to the catalytic converter), you may hear rattling noises coming from underneath your vehicle when accelerating or decelerating quickly.
4. Check for warning lights on the dashboard: Many modern vehicles are equipped with sensors that detect problems with their emissions systems and will display warning lights on their dashboards when something isn’t working correctly – including issues with their catalytic converters – so check for any illuminated warning lights before attempting any repairs yourself or taking it to a mechanic shop.
The Cost of Replacing a Catalytic Converter in Your Vehicle
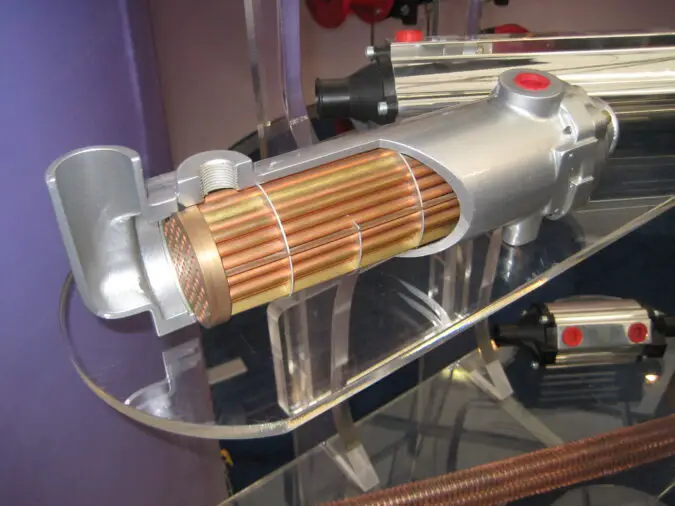
“Catalytic Converter” by Hiddenpower is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 2.0
The cost of replacing a catalytic converter in your vehicle can vary greatly depending on the make and model of your car. Generally, the cost of a replacement catalytic converter ranges from $400 to $2,000. The exact price will depend on the type of vehicle you have and the complexity of installation.
In addition to the cost of purchasing a new catalytic converter, there may be additional labor costs associated with its installation. Depending on your vehicle’s make and model, it may require special tools or expertise to install it correctly. This could add an additional $100-$500 to the total cost.
It is important to note that some states have laws requiring vehicles with certain emissions levels to have their catalytic converters replaced at regular intervals for them to pass inspection tests. If this is applicable in your state, then you may be required by law to replace your catalytic converter even if it is still functioning properly.
Finally, if you are considering replacing your own catalytic converter instead of having it done professionally, keep in mind that this can be a difficult job that requires specialized tools and knowledge about how cars work. It is not recommended unless you are confident in your ability as an experienced mechanic or auto technician.
Understanding the Different Types of Catalytic Converters Available for Cars
Catalytic converters are an important part of a car’s exhaust system, as they help reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere. There are several different types of catalytic converters available for cars, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Understanding the differences between these types can help you make an informed decision when selecting a converter for your vehicle.
- The most common type of catalytic converter is the three-way converter, which is designed to reduce emissions from hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and nitrogen oxides (NOx). This type of converter uses a combination of precious metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium to convert these pollutants into harmless gases like nitrogen and water vapor. Three-way converters are typically found on gasoline-powered vehicles manufactured after 1975.
- Another type of catalytic converter is the two-way converter, which is designed to reduce HC and CO emissions only. This type does not contain any precious metals and instead relies on chemical reactions between oxygen in the exhaust gas stream and HC or CO molecules to convert them into harmless gases like carbon dioxide (CO2) or water vapor. Two-way converters are typically found on diesel engines manufactured after 1993.
- Finally, there are oxidation catalysts that do not contain any precious metals but instead use chemical reactions between oxygen in the exhaust gas stream and HC or CO molecules to convert them into harmless gases like carbon dioxide (CO2) or water vapor without reducing NOx emissions at all. Oxidation catalysts are typically used in older vehicles that do not have three-way converters installed due to their lower cost compared to other types of converters.
In conclusion, there are several different types of catalytic converters available for cars depending on their age and engine type: three-way converters for gasoline engines manufactured after 1975; two-way converters for diesel engines manufactured after 1993; oxidation catalysts for older vehicles without three-way systems installed due to their lower cost compared with other types of catalysis systems.
The Impact of Removing or Replacing a Car’s Catalytic Converter on Emissions Tests
The catalytic converter is an essential component of a car’s exhaust system. It helps to reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere by converting them into less harmful substances. As such, it plays an important role in helping to reduce air pollution and meet emissions standards.
Removing or replacing a car’s catalytic converter can have a significant impact on emissions tests. Without the presence of this device, more pollutants will be released into the atmosphere, resulting in higher levels of carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC), and nitrogen oxides (NOx).
This can lead to increased levels of smog and other air quality issues. Additionally, without a functioning catalytic converter, cars may fail their emissions tests due to high levels of these pollutants. In some cases, replacing an old or damaged catalytic converter with a new one may help improve emissions test results by reducing pollutant levels back within acceptable limits.
However, it is important to note that not all aftermarket converters are created equal; some may not be as effective at reducing pollutant levels as OEM converters and could potentially result in higher-than-expected emission readings during testing.
Overall, removing or replacing a car’s catalytic converter can have serious implications for its performance on emissions tests and should only be done when absolutely necessary with caution taken when selecting replacement parts.
What Are the Environmental Benefits of Having a Working Catalytic Converter?
A catalytic converter is an important component of a vehicle’s exhaust system, as it helps to reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the environment. The primary environmental benefit of having a working catalytic converter is that it reduces emissions of carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides.
- Carbon monoxide is a colorless and odorless gas that can be toxic when inhaled in large amounts. It contributes to air pollution and can cause health problems such as headaches, dizziness, nausea, and even death in extreme cases. A working catalytic converter helps to reduce the amount of carbon monoxide released into the atmosphere by converting it into less harmful compounds such as carbon dioxide and water vapor.
- Hydrocarbons are organic compounds made up of hydrogen and carbon atoms that are found in gasoline vapors. They contribute to smog formation when they react with nitrogen oxides in sunlight. A functioning catalytic converter helps reduce hydrocarbon emissions by converting them into less harmful substances such as water vapor or oxygen molecules.
- Nitrogen oxides are gases composed of nitrogen and oxygen atoms that form when fuel is burned at high temperatures during combustion processes like those used in cars or power plants. These gases contribute to smog formation which can lead to respiratory problems for humans if inhaled over long periods. A working catalytic converter helps reduce these emissions by converting them into harmless nitrogen gas molecules which disperse harmlessly into the atmosphere without contributing to air pollution or health risks for humans or animals alike.
Is It Legal to Drive Without a Working Catalytic Converter?
No, it is not legal to drive without a working catalytic converter. Catalytic converters are an important part of a vehicle’s emissions control system and are required by law in most states. A catalytic converter helps reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere from a vehicle’s exhaust system.
Without one, vehicles can emit up to ten times more pollutants than allowed by law. In addition to being illegal, driving without a working catalytic converter can also be dangerous for both the driver and other motorists on the road.
The increased emissions from an improperly functioning exhaust system can cause visibility issues for other drivers due to smoke or fumes coming from the vehicle’s tailpipe. This could lead to accidents or other hazardous situations on the roadways.
If your vehicle does not have a functioning catalytic converter, it is important that you have it replaced as soon as possible to comply with state laws and ensure your safety while driving.
Tips for Maintaining and Extending the Life of Your Car’s Catalytic Converter
1. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule: Regularly servicing your car according to the manufacturer’s recommendations is essential for keeping your catalytic converter in good condition. This includes changing the oil and filter, checking and replacing spark plugs, and inspecting other components such as air filters, fuel filters, and exhaust systems.
2. Use high-quality fuel: Using low-quality or contaminated fuel can cause damage to your catalytic converter over time. Make sure you use only high-quality gasoline that meets the standards of your vehicle’s manufacturer.
3. Avoid running on empty: Running out of gas can cause debris to build up in the catalytic converter which can lead to clogging or damage over time. Make sure you always keep a full tank of gas to avoid this problem from occurring.
4. Keep an eye on engine performance: If you notice any changes in engine performance such as decreased power or increased emissions it could be a sign that something is wrong with your catalytic converter and should be checked by a professional mechanic immediately before further damage occurs.
5. Drive responsibly: Aggressive driving habits such as rapid acceleration or hard braking can put extra strain on your car’s engine which can lead to premature wear on its components including the catalytic converter over time so make sure you drive responsibly at all times.

