- How Does a Catalytic Converter Work
- Different Types of Catalytic Converters
- Role of Platinum in a Catalytic Converter
- If Your Car Has a Faulty Catalytic Converter
- High-Performance Catalytic Converter
- Extend the Life of Your Catalytic Converter
- Common Problems With Catalytic Converters
- Clean and Maintain Your Exhaust System
- OEM And Aftermarket Replacement Parts
- Have Regular Maintenance Checks
How Does a Catalytic Converter Work?
So, what is inside a catalytic converter? A catalytic converter is an important component of a vehicle’s exhaust system. It is designed to reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere by converting them into less harmful substances.
The catalytic converter works by using a combination of chemical reactions and physical processes to convert toxic gases, such as carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons, into harmless compounds like carbon dioxide and water vapor.
The catalytic converter consists of two main components: a catalyst substrate and a catalyst coating. The substrate is typically made from ceramic or metal honeycomb structures that provide a large surface area for the reaction to take place on.
The catalyst coating is usually composed of precious metals such as platinum, palladium, or rhodium which act as the active sites for the chemical reactions that occur within the converter. To learn more about these precious metals, check out our guide on which catalytic converters have the most rhodium, as well as how much platinum is in a catalytic converter.
When exhaust gases enter the catalytic converter they are exposed to high temperatures which cause them to react with oxygen in presence of these precious metals. This reaction causes pollutants like carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons to be converted into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide and water vapor before being released out through the tailpipe.
The efficiency of this process depends on several factors including temperature, air-fuel ratio, engine speed, load conditions, etc., so it’s important that all these parameters are kept within their optimal range for maximum efficiency from your vehicle’s catalytic converter system.
What Are the Different Types of Catalytic Converters?
Catalytic converters are an important part of a vehicle’s exhaust system, as they reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere. There are several different types of catalytic converters available, each designed to meet specific needs and requirements.
- The most common type is the three-way catalytic converter, which is designed to reduce emissions from gasoline engines. This type of converter uses a combination of platinum, palladium, and rhodium to convert carbon monoxide (CO) into carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrocarbons (HC) into the water, and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into nitrogen gas.
- Another type is the diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC), which is used in diesel engines to reduce emissions such as particulate matter and hydrocarbons. This type uses a combination of platinum and palladium to oxidize HCs and COs into CO2 and water vapor.
- The selective catalytic reduction (SCR) converter is used in diesel engines to reduce NOx emissions by converting them into harmless nitrogen gas using urea or ammonia as a reducing agent. The SCR also helps improve fuel economy by reducing engine backpressure caused by NOx buildup in the exhaust system.
Finally, there are lean NOx traps (LNTs), which use zeolite-based materials such as barium oxide or potassium oxide to trap NOx molecules until they can be converted back into harmless nitrogen gas through thermal regeneration or active regeneration with fuel additives like ethanol or methanol injection systems.
LNTs are typically used in light-duty vehicles that have gasoline direct injection systems or turbocharged engines that produce higher levels of NOx than traditional gasoline engines do. This should give you a better understanding of what is inside a catalytic converter.
What Is the Role of Platinum in a Catalytic Converter?
The role of platinum in a catalytic converter is to act as a catalyst, which is an agent that accelerates the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. Platinum is used because it has high activity and stability at high temperatures, making it ideal for use in catalytic converters.
In these devices, platinum helps convert harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide and water vapor. This process helps reduce air pollution by reducing the number of toxic gases released into the atmosphere.
How Can You Tell If Your Car Has a Faulty Catalytic Converter?
A faulty catalytic converter can cause a variety of issues with your car. The most common signs that your car has a faulty catalytic converter include decreased engine performance, increased exhaust emissions, and an illuminated check engine light.
- Decreased engine performance is one of the most common signs that your car has a faulty catalytic converter. This can manifest itself in several ways, such as reduced acceleration or power when driving, difficulty starting the vehicle, or even stalling while idling.
- Increased exhaust emissions are another sign that your car may have a faulty catalytic converter. If you notice an increase in smoke coming from the tailpipe or an unusual smell coming from the exhaust system, it could be due to a malfunctioning catalytic converter.
- Finally, if you notice that your check engine light is illuminated on the dashboard of your vehicle then this could indicate that there is an issue with the catalytic converter as well. It is important to take note of any warning lights on your dashboard and have them checked out by a professional mechanic as soon as possible to ensure the proper functioning of all components in your vehicle’s system.
What Are the Benefits of Installing a High-Performance Catalytic Converter?
Installing a high-performance catalytic converter offers numerous benefits to vehicle owners. The most important benefit is improved fuel economy. High-performance catalytic converters are designed to reduce the number of harmful emissions released into the atmosphere, which in turn reduces fuel consumption.
Additionally, these converters can help improve engine performance by reducing exhaust backpressure and increasing horsepower and torque output. Furthermore, they can also reduce engine noise levels and provide a smoother ride due to their superior construction materials and design.
Finally, installing a high-performance catalytic converter (or a high-flow catalytic converter) can extend the life of your vehicle’s exhaust system by preventing corrosion caused by excessive heat or moisture buildup in the exhaust system.
How Can You Extend the Life of Your Car’s Catalytic Converter?
The catalytic converter is an important part of a car’s exhaust system, as it helps to reduce the number of harmful emissions released into the atmosphere. It is essential to maintain and extend the life of your car’s catalytic converter to ensure that your vehicle runs efficiently and safely. Here are some tips for extending the life of your car’s catalytic converter:
1. Regularly check and replace spark plugs: Spark plugs are responsible for igniting fuel in the engine, so it is important to regularly check them for wear and tear. If they become worn or damaged, they can cause misfires which can damage the catalytic converter over time.
2. Use high-quality fuel: Using low-quality fuel can lead to deposits building up on the walls of your engine’s cylinders, which can eventually clog up your catalytic converter. To avoid this problem, use only high-quality fuels with a higher octane rating than what is recommended by your vehicle manufacturer.
3. Avoid running on empty: Running out of gas often causes dirt and debris from inside the tank to enter into the fuel system, which can clog up or damage components such as spark plugs or even worse –the catalytic converter itself. To avoid this problem, always make sure you have enough gas in your tank before setting off on a journey.
4. Have regular tune-ups: Having regular tune-ups will help keep all parts of your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently – including its exhaust system. During these tune-ups, any worn or damaged parts should be replaced immediately to prevent further damage from occurring down the line – including damage caused by faulty spark plugs or other components that could affect performance levels within an exhaust system such as a catalytic converter.
5. Check oxygen sensors regularly: Oxygen sensors measure how much oxygen is present in an engine’s exhaust gases, allowing it to adjust its air/fuel mixture accordingly. If these sensors become faulty, they may not be able to detect when too much-unburned fuel enters into an engine’s cylinders, leading directly towards increased levels of pollution being emitted from its tailpipe – something that could potentially harm both people’s health as well as damaging a car’s own internal components such as its catalyst converters. Therefore, it is important that these sensors are checked regularly during routine maintenance checks.
What Are Some Common Problems With Aftermarket Catalytic Converters?
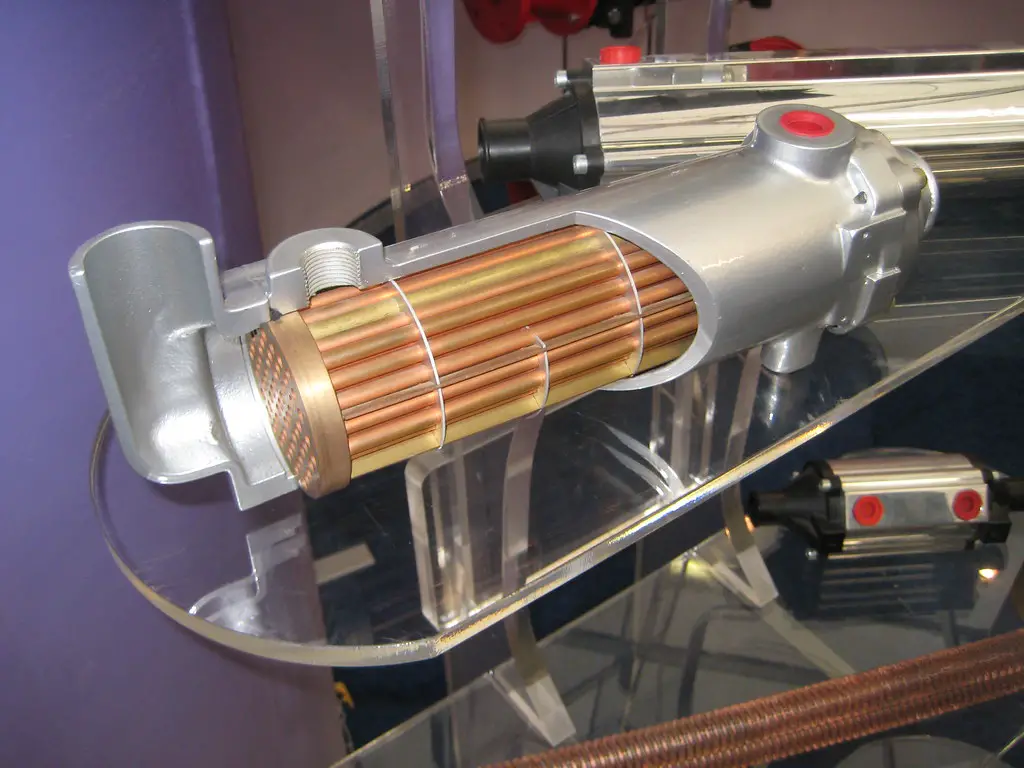
“Catalytic Converter” by Hiddenpower is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 2.0
Aftermarket catalytic converters can present a number of issues. One common problem is that they may not be designed to meet the same standards as OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) catalytic converters, meaning they may not be as effective at reducing emissions.
Additionally, aftermarket catalytic converters may not fit properly on the vehicle, leading to exhaust leaks and other problems. Furthermore, aftermarket catalytic converters are often made from lower-quality materials than OEM parts and can fail prematurely or become clogged more easily.
So, be wary of the symptoms of a clogged catalytic converter, as well as figure out whether can a bad catalytic converter cause a misfire. Finally, some aftermarket catalytic converters are illegal in certain states due to their lack of effectiveness in reducing emissions. This will be best understood once you’ve learned what is inside a catalytic converter.
How Do You Clean and Maintain Your Car’s Exhaust System and Its Components
Maintaining your car’s exhaust system is essential for ensuring its performance and longevity. The catalytic converter, in particular, is an important component of the exhaust system that helps reduce emissions and should be regularly inspected and cleaned. Here are some tips on how to clean and maintain your car’s exhaust system:
1. Inspect the Exhaust System: Regularly inspect the entire exhaust system for any signs of damage or corrosion to the catalytic converter. Look for any holes, cracks, or rust spots that may indicate a problem with the pipes or muffler. If you notice any issues, have them repaired as soon as possible to prevent further damage to other components of the exhaust system.
2. Clean Your Catalytic Converter: The catalytic converter can become clogged over time due to buildup from fuel additives or oil deposits from engine wear and tear. To clean it, use a specialized cleaning solution or a catalytic converter cleaner designed specifically for this purpose; follow all instructions carefully when using these products as they can be hazardous if not used properly.
3. Replace Worn Parts: Over time, parts such as gaskets and hangers may become worn out due to age or exposure to extreme temperatures; replace these parts when necessary to keep your car running smoothly and efficiently without compromising safety standards set by manufacturers.
4. Check Emissions Levels: Have your vehicle tested regularly at an authorized testing center to ensure that it meets local emissions standards; this will help you avoid costly fines associated with non-compliance.
By following these steps regularly you can ensure that your car’s exhaust system remains in good condition (especially when you know what is inside a catalytic converter) so it can continue performing optimally while helping reduce harmful emissions into our environment.
What Is The Difference Between OEM And Aftermarket Replacement Parts For A Vehicle’s Exhaust System
The primary difference between OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) and aftermarket replacement parts for a vehicle’s exhaust system, including the catalytic converter, is the quality of the parts. OEM parts are designed and manufactured to meet or exceed the original specifications of the vehicle manufacturer, while aftermarket parts may not be held to such stringent standards.
Additionally, OEM parts are typically more expensive than aftermarket alternatives due to their higher quality and longer lifespan. OEM exhaust systems are designed with specific materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and vibrations over time without degrading in performance or reliability.
Aftermarket exhaust systems may use lower-grade materials that can corrode or break down more quickly than those used in an OEM system. Furthermore, some aftermarket converters may not meet emissions standards set by local governments or regulatory agencies.
In conclusion, when replacing a vehicle’s exhaust system components including its catalytic converter (and knowing what is inside a catalytic converter) it is important to consider both cost and quality when selecting either an OEM or aftermarket part.
Why Is It Important To Have Regular Maintenance Checks On Your Vehicle’s Exhaust System
Having regular maintenance checks on your vehicle’s exhaust system is important for a number of reasons. The exhaust system is responsible for controlling the emissions from your vehicle, and ensuring that they are within legal limits.
If the emissions exceed legal limits, you may be subject to fines or other penalties. Additionally, regular maintenance checks can help to identify any potential problems with the exhaust system (as well as what is inside a catalytic converter) before they become more serious and costly to repair.
The catalyst converter is an important component of the exhaust system as it helps to reduce harmful pollutants in the exhaust gases by converting them into less harmful substances. Regular maintenance checks can help ensure that this component is functioning correctly and efficiently, helping to reduce emissions even further.
Other components of the exhaust system such as mufflers and pipes should also be checked regularly for signs of wear or damage which could lead to leaks or other issues with performance. Regular maintenance checks can help identify these issues early on so that they can be addressed before becoming more serious problems down the line.
In summary, having regular maintenance checks on your vehicle’s exhaust system including its catalyst converter and other components is important to ensure that emissions remain within legal limits, as well as identifying any potential problems with performance before they become more serious issues requiring costly repairs.

