- How Does a Catalytic Converter Work
- Different Types of Catalytic Converters
- Chemistry Behind Catalytic Converters
- Platinum, Palladium, and Rhodium
- Diagnose a Bad Catalytic Converter
- Aftermarket vs OEM Catalytic Converters
- Shopping for a New or Used Catalytic Converter
- Causes of Damage to Your Catalytic Converter
- Maintaining Your Car’s Performance
- What’s The Environmental Impact
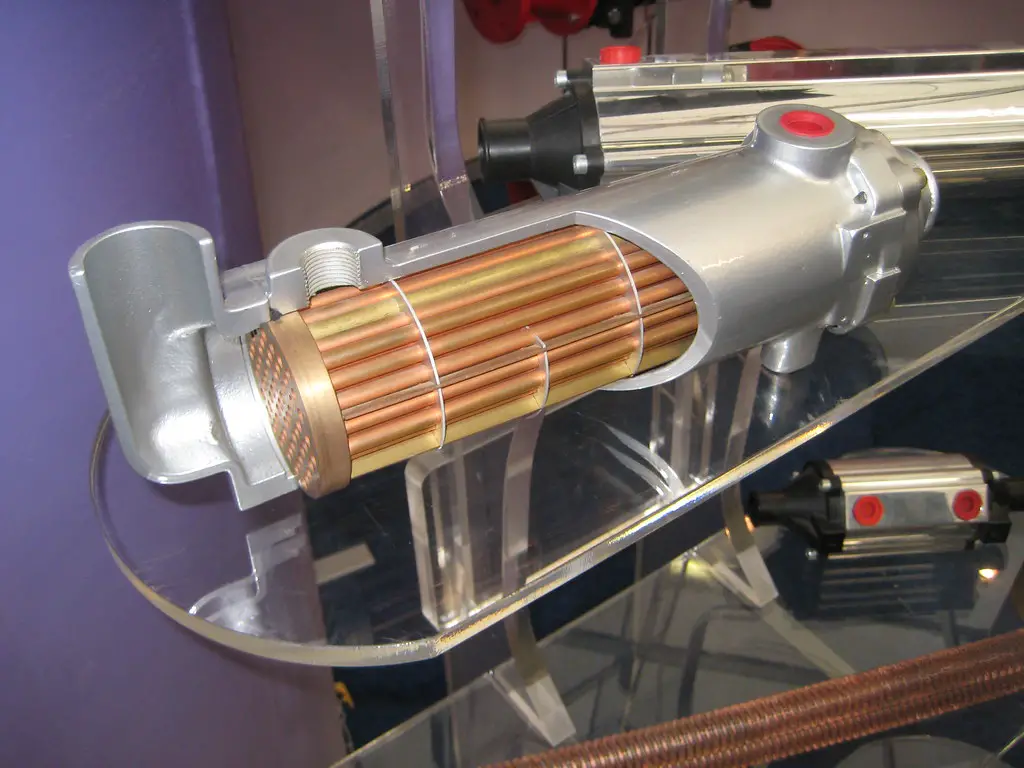
What is a Catalytic Converter and How Does it Work?
So, what’s in catalytic converters? A catalytic converter is an emissions control device that is fitted to the exhaust system of a vehicle. It works by converting harmful pollutants in the exhaust gases into less harmful substances before they are released into the atmosphere.
The catalytic converter does this by using a catalyst, usually platinum or palladium, to chemically convert the pollutants into carbon dioxide and water vapor. The catalytic converter works by passing exhaust gases through a honeycomb-like structure coated with precious metals such as platinum and palladium.
These metals act as a catalyst, which means they speed up chemical reactions without being consumed themselves. If you want to learn more about these precious metals, check out our explainer on which catalytic converters have the most rhodium, as well as how much platinum is in a catalytic converter.
As the exhaust gases pass through this structure, they come into contact with these metals and undergo chemical reactions that convert them from harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and hydrocarbons (HC) into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O). This process helps reduce air pollution caused by vehicle emissions.
In addition to reducing air pollution, catalytic converters also help improve fuel efficiency by allowing engines to run more efficiently at lower temperatures. This is because when an engine runs at higher temperatures it produces more NOx which can be damaging to both human health and the environment if not properly controlled.
By controlling these emissions with a catalytic converter, engines can run more efficiently while still producing fewer pollutants than before. If you’re thinking about scrapping your car, you could also check out our guide on the catalytic converter precious metal scrap prices.
The Different Types of Catalytic Converters and Their Benefits
Catalytic converters are an essential part of a vehicle’s exhaust system. They are designed to reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere by converting them into less harmful substances. There are several different types of catalytic converters available, each with its own unique benefits.
- The most common type is the three-way catalytic converter, which is used in gasoline-powered vehicles. This type of converter uses a combination of platinum, palladium, and rhodium to convert carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons (HC) into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O). The three-way catalytic converter also reduces nitrogen oxide emissions (NOx), making it one of the most effective pollution control devices available for gasoline engines.
- Another type is the diesel oxidation catalyst, which is used in diesel engines. This device works by oxidizing unburned hydrocarbons and reducing particulate matter from diesel exhaust gases. It also helps reduce NOx emissions from diesel engines as well as other pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO2).
- The last type is the selective catalytic reduction system, or SCR system for short. This device uses urea or ammonia to reduce NOx emissions from both gasoline and diesel engines by up to 90%. It can also help improve fuel economy by up to 5%.
Each type of catalytic converter has its own unique benefits that make it suitable for different applications depending on your needs. All types offer improved air quality while helping you save money on fuel costs at the same time.
Understanding the Chemistry Behind Catalytic Converters
Catalytic converters are an essential component of modern automobiles, helping to reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere. Understanding the chemistry behind these devices is key to appreciating their importance and effectiveness.
At its core, a catalytic converter is a device that uses a chemical reaction to convert toxic exhaust gases into less harmful substances. The process involves three main components: an oxidation catalyst, a reduction catalyst, and an adsorption catalyst.
The oxidation catalyst is responsible for converting carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons (HC) into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O). This reaction occurs when oxygen molecules in the exhaust gas react with CO and HC molecules at high temperatures. The result is two harmless byproducts: CO2 and H2O.
The reduction catalyst works in tandem with the oxidation catalyst to further reduce emissions by converting nitrogen oxides (NOx) into nitrogen gas (N2). This reaction occurs when NOx molecules react with hydrogen atoms at high temperatures, resulting in N2 as a byproduct.
Finally, the adsorption catalyst helps capture any remaining pollutants before they can escape out of the tailpipe. It does this by trapping particles on its surface until they can be burned off during normal engine operation or removed during periodic maintenance intervals.
By combining these three components together in one device, catalytic converters can effectively reduce emissions from automobiles without sacrificing performance or fuel economy. As such, they have become an indispensable part of modern automotive technology—helping us keep our air clean while still enjoying all that cars have to offer.
The Role of Platinum, Palladium, and Rhodium in Catalytic Converters
Catalytic converters are an essential component of modern automobiles, as they help reduce the number of harmful emissions released into the atmosphere. These devices rely on a combination of precious metals, such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium, to convert toxic gases into less harmful substances.
- Platinum is the most commonly used metal in catalytic converters due to its ability to efficiently oxidize carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons. It also helps reduce nitrogen oxide emissions by converting them into nitrogen and oxygen molecules.
- Palladium is another important metal used in catalytic converters because it can effectively reduce carbon monoxide levels while also helping to control hydrocarbon emissions.
- Finally, rhodium is used in some catalytic converters because it has a higher oxidation potential than either platinum or palladium and can therefore help further reduce emissions levels.
The three metals work together to create a chemical reaction that breaks down pollutants before they are released into the atmosphere. Platinum acts as an oxidizing agent that converts carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons into harmless water vapor and carbon dioxide molecules; palladium helps break down nitrogen oxide molecules; while rhodium further reduces emission levels by increasing oxidation potentials within the converter itself.
In summary, platinum, palladium, and rhodium play an important role in catalytic converters by helping convert toxic gases into less harmful substances before they are released into the environment. The combination of these three metals allows for efficient conversion rates that help protect our air quality from dangerous pollutants emitted from automobiles.
How to Diagnose Problems with Your Car’s Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter is an important part of a car’s exhaust system, as it helps to reduce the number of harmful emissions released into the atmosphere. If your car’s catalytic converter is not functioning properly, it can cause a variety of problems with your vehicle. To diagnose and repair any issues with your car’s catalytic converter, you will need to follow these steps:
1. Check for engine misfires or rough idling. A malfunctioning catalytic converter can cause engine misfires or rough idling due to an accumulation of unburned fuel in the exhaust system. If you notice either of these symptoms, it could be a sign that there is something wrong with your car’s catalytic converter. You can learn more in our write-up on whether can a bad catalytic converter cause a misfire.
2. Inspect the oxygen sensor readings on your vehicle’s computer system. The oxygen sensor monitors how much oxygen is present in the exhaust gases and sends this information back to the computer system for it to adjust fuel delivery accordingly. If there are any discrepancies between what should be normal readings and what is actually being read by the computer, then this could indicate that there may be an issue with your car’s catalytic converter.
3. Look for signs of physical damage to the catalytic converter on the outside of the unit itself such as cracks or holes in its casing or discoloration from heat damage caused by excessive temperatures inside its chamber due to clogged passages within its honeycomb structure which can lead to reduced efficiency and performance levels from its intended purpose as well as increased emissions output from unburned fuel passing through without being converted into harmless gasses like carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O).
4. Have a professional mechanic inspect and test your vehicle’s exhaust system using specialized diagnostic equipment such as an OBD-II scanner which can detect any faults within various components including those related directly or indirectly related to a faulty catalytic converter like air/fuel ratio sensors, mass airflow sensors, etc., so they can accurately pinpoint where exactly any issues may lie before attempting repairs or replacements if necessary.
The Pros and Cons of Aftermarket vs OEM Catalytic Converters

“CRX b-pipe and catalytic converter” by CrowzRSA is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
Catalytic converters are an important part of a vehicle’s exhaust system, as they help reduce emissions and improve air quality. When it comes to replacing a catalytic converter, there are two main options available: aftermarket or original equipment manufacturer (OEM). Each option has its own advantages and disadvantages that should be considered before making a purchase.
Pros of Aftermarket Catalytic Converters
The primary advantage of aftermarket catalytic converters is cost. Aftermarket converters tend to be significantly cheaper than OEM models, making them an attractive option for those on a budget. Additionally, aftermarket converters often come with warranties that can provide peace of mind in the event of any issues with the product.
Cons of Aftermarket Catalytic Converters
The biggest disadvantage associated with aftermarket catalytic converters is their lack of reliability compared to OEM models. While some aftermarket products may perform just as well as their OEM counterparts, others may not meet the same standards in terms of durability or efficiency.
Additionally, some states have laws prohibiting the use of non-OEM parts on vehicles registered within their borders; this could limit your ability to install an aftermarket converter even if you wanted to do so.
Pros of OEM Catalytic Converters
The primary benefit associated with purchasing an OEM catalytic converter is reliability; these parts are designed specifically for your vehicle’s make and model and will fit perfectly without any modifications required.
Additionally, many states require that vehicles use only genuine parts when undergoing emissions testing; using an OEM part can help ensure compliance with these regulations while also providing peace of mind knowing that you have installed a quality product on your vehicle.
Cons Of OEM Catalytic Converter
The main downside associated with purchasing an OEM catalytic converter is cost; these parts tend to be more expensive than their aftermarket counterparts due to higher production costs and brand recognition premiums charged by manufacturers for using genuine parts in repairs or replacements.
Additionally, some older vehicles may no longer have replacement parts available from the manufacturer due to discontinuation or obsolescence; this could leave you stuck having to purchase used components from third-party sources which could potentially lead to further complications down the line if they don’t fit properly or fail prematurely due to age or wear & tear issues not covered by warranty policies offered by third-party vendors.
What to Look for When Shopping for a New or Used Catalytic Converter
When shopping for a new or used catalytic converter, there are several factors to consider. First, it is important to make sure the converter is compatible with your vehicle’s make and model. Additionally, you should check that the converter meets all applicable emissions standards for your area.
It is also important to inspect the condition of any used catalytic converters before purchasing them. Look for signs of damage such as rust or corrosion on the exterior of the unit, as well as any visible cracks or holes in its housing. Additionally, check that all mounting hardware is included and in good condition.
Finally, be sure to research different brands and models of catalytic converters before making a purchase decision. Compare prices between different sellers and read customer reviews online to ensure you are getting a quality product at a fair price.
Common Causes of Damage to Your Car’s Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter is an essential component of a vehicle’s exhaust system, as it helps to reduce the number of harmful emissions released into the atmosphere. Unfortunately, this part can be prone to damage due to a variety of causes. Here are some of the most common reasons for damage to your car’s catalytic converter:
1. Overheating: The catalytic converter works by converting toxic gases into less harmful substances through a chemical reaction that produces heat. If the engine is running too hot or if there is an issue with the cooling system, this can cause excessive heat in the exhaust system and lead to damage to the catalytic converter. You can confirm this with a catalytic converter temperature test.
2. Contamination: Foreign objects such as oil or fuel can enter into and clog up the exhaust system, leading to blockages that prevent proper airflow and cause overheating in the catalytic converter.
3. Faulty spark plugs: If spark plugs are not firing correctly, they may produce too much-unburned fuel which will pass through and overheat your car’s catalytic converter.
4. Poor maintenance: Regular maintenance such as changing oil filters and spark plugs on time can help prevent issues with your car’s exhaust system that could lead to damage in its catalytic converter over time.
By understanding these common causes of damage, you can take steps toward preventing them from occurring to keep your vehicle running smoothly for years to come.
Tips for Maintaining Your Car’s Performance with a Properly Functioning Catalyst Converter
1. Ensure Regular Maintenance: It is important to ensure that your car receives regular maintenance, including oil changes and tune-ups, to keep the catalyst converter functioning properly. This will help prevent any build-up of dirt or debris that can clog the converter and reduce its efficiency.
2. Use High-Quality Fuel: Using high-quality fuel with a low sulfur content can help reduce the number of pollutants released from your vehicle’s exhaust system, which in turn helps keep the catalyst converter working efficiently.
3. Check for Leaks: Make sure to check for any leaks in your exhaust system on a regular basis as these can cause damage to the catalyst converter over time if left unchecked.
4. Avoid Overloading Your Vehicle: Overloading your vehicle with too much weight or cargo can put extra strain on the engine and exhaust system, which may lead to problems with the catalyst converter over time if not addressed promptly.
5. Monitor Your Driving Habits: Aggressive driving habits such as rapid acceleration or hard braking can put extra strain on your engine and exhaust system, leading to problems with the catalytic converter over time if not monitored closely enough. Try to drive more smoothly whenever possible to maintain optimal performance from your vehicle’s catalytic converter system.
Environmental Impact: Why It’s Important to Have an Efficiently Working Catalyst Converter
Catalytic converters are an essential component of modern vehicles, as they help reduce the number of harmful emissions released into the environment. The catalytic converter works by converting toxic gases such as carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons into less harmful substances like nitrogen and water vapor.
This process helps to reduce air pollution, which can have a significant impact on human health and the environment.
- Having an efficiently working catalyst converter is important for several reasons. First, it helps to ensure that vehicles are emitting fewer pollutants into the atmosphere. This reduces smog levels in cities and towns, which can lead to improved air quality and fewer respiratory illnesses in people living nearby. Additionally, reducing emissions from cars also helps to slow down climate change by reducing greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere.
- Second, having an efficient catalyst converter also helps improve fuel economy in vehicles since it reduces exhaust backpressure on engines. This means that engines don’t have to work as hard when running at higher speeds or under heavy loads, resulting in better fuel efficiency overall. In addition to saving money on fuel costs for drivers, this also reduces overall emissions from cars since they use less gasoline over time due to improved efficiency levels.
- Finally, having an efficient catalyst converter is important because it ensures that vehicles meet current emission standards set by governments around the world for road-going automobiles. Without these standards being met through properly functioning catalytic converters, manufacturers would be unable to sell their products legally or safely on public roads without risking hefty fines or other penalties from regulatory bodies like EPA (Environmental Protection Agency).
In conclusion, having an efficiently working catalyst converter is essential for protecting both human health and our environment from dangerous pollutants released by automobiles every day across the globe. Not only does this help reduce smog levels in cities and towns but it also improves fuel economy while ensuring that manufacturers meet current emission standards.