- The Anatomy of a Catalytic Converter
- How to Identify a Catalytic Converter
- Benefits of Installing a Catalytic Converter
- Materials Used in the Catalytic Converter
- Problems with Catalytic Converters
- Different Types of Catalytic Converters
- Oxygen Sensors in Regulating Emissions
- Comparing OEM and Aftermarket Options
- Maintaining Your Catalytic Converter
- Latest Innovations in Automotive Technology
Exploring the Anatomy of a Catalytic Converter
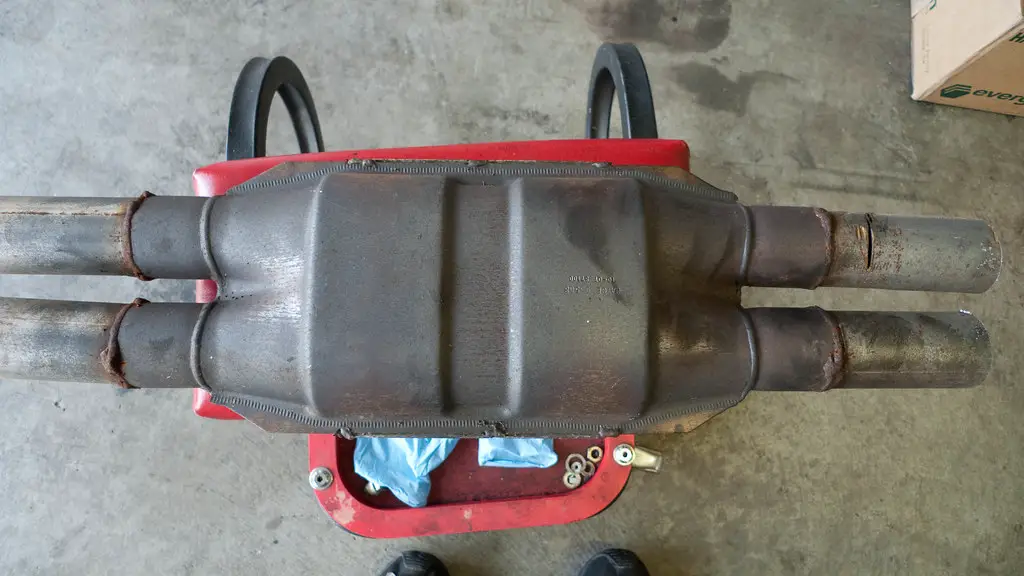
The catalytic converter is an essential component of a vehicle’s exhaust system. It is designed to reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere by converting them into less harmful substances. This article will explore the anatomy of a catalytic converter (and what does a catalytic converter look like) and how it works to reduce emissions.
A catalytic converter consists of three main components: a substrate, catalyst, and housing. The substrate is typically made from ceramic or metal and serves as the base for the catalyst material. The catalyst material is usually composed of platinum, palladium, or rhodium and helps to break down pollutants in the exhaust gases as they pass through it.
For more insight, you can learn more in our explainer on which catalytic converters have the most rhodium, as well as how much platinum is in a catalytic converter. Finally, the housing encloses these components and provides protection from heat and other environmental factors that could damage them over time.
When exhaust gases enter a catalytic converter, they are forced through small channels in its substrate material where they come into contact with its catalyst material. As this happens, chemical reactions take place which convert harmful pollutants such as carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons (HC) into less hazardous substances like carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O).
This process helps to reduce air pollution levels significantly when compared to vehicles without converters installed on their exhaust systems. In addition to reducing emissions levels, catalytic converters also help improve fuel efficiency by allowing engines to run more efficiently at lower temperatures than would otherwise be possible without one installed on their exhaust system.
This can result in significant savings for drivers over time due to reduced fuel costs associated with improved engine performance. You can learn more in our guide on what does the catalytic converter do, in addition to how does a catalytic converter work.
Overall, understanding how a catalytic converter works (and what does a catalytic converter look like) can help drivers make informed decisions about their vehicle’s maintenance needs while also helping protect our environment from dangerous air pollution levels caused by vehicle emissions.
How to Identify a Catalytic Converter
A catalytic converter is an important part of a vehicle’s exhaust system. It helps reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere by converting them into less harmful substances. Identifying a catalytic converter can be done by looking for certain characteristics and features.
The most obvious way to identify a catalytic converter is by its shape and size. It is typically cylindrical in shape, with two pipes extending from either end. The pipes are usually made of stainless steel or aluminum, and they may have heat shields attached to them.
The overall length of the converter will vary depending on the make and model of vehicle it is installed in, but it should be roughly between 8-12 inches long. Another way to identify a catalytic converter is by its location in the exhaust system. It will usually be located near the engine block or close to where the exhaust pipe meets up with the muffler assembly.
In some cases, it may also be found further down along the exhaust pipe before it exits out through your tailpipe at the rear of your vehicle. Unless you have a catalytic converter with an integrated exhaust manifold.
Finally, you can also look for any markings that may indicate that what you are looking at is indeed a catalytic converter. Many converters will have an identifying label or stamp on them that includes information such as their manufacturer name or part number as well as other details about their construction materials and design specifications.
By taking note of these characteristics and features (as well as what does a catalytic converter look like), you should be able to easily identify whether what you are looking at is indeed a catalytic converter or not.
The Benefits of Installing a Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter is an important component of a vehicle’s exhaust system. It helps to reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere by converting them into less harmful substances. Installing a catalytic converter can provide numerous benefits, both for the environment and for your vehicle.
- One of the primary benefits of installing a catalytic converter is that it helps to reduce air pollution. The device works by converting toxic gases such as carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons into less harmful substances like nitrogen and water vapor. This reduces the number of pollutants released into the atmosphere, helping to improve air quality in urban areas where air pollution is often an issue.
- Another benefit of installing a catalytic converter is that it can help improve fuel efficiency in your vehicle. Reducing emissions, it allows your engine to run more efficiently, which can result in improved fuel economy over time. This can save you money on gas costs while also helping to reduce your environmental impact at the same time.
- Finally, installing a catalytic converter can help extend the life of your vehicle’s engine by reducing wear and tear on its components due to reduced emissions levels. This means that you may be able to avoid costly repairs or replacements down the line due to reduced strain on your engine caused by excessive emissions levels from not having a properly functioning exhaust system with a working catalytic converter installed in it.
Overall, there are many advantages associated with installing a catalytic converter in your vehicle’s exhaust system including improved air quality, increased fuel efficiency, and extended engine life expectancy due to reduced wear and tear caused by excessive emissions levels without one installed properly functioning one installed correctly.
What Materials are Used in the Construction of a Catalytic Converter?
Catalytic converters are an important component of modern vehicle exhaust systems. They are designed to reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere by converting them into less harmful substances.
The materials used in the construction of a catalytic converter include a ceramic or metal honeycomb substrate, precious metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium, and other materials such as aluminum oxide and silicon carbide.
The ceramic or metal honeycomb substrate is typically made from cordierite or stainless steel. This substrate provides a large surface area for the catalysts to adhere to and helps ensure that exhaust gases flow evenly through the converter.
Precious metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium act as catalysts that help convert pollutants into less harmful substances. These metals are usually applied in very thin layers onto the substrate using a process called thermal spraying.
Other materials used in catalytic converters include aluminum oxide and silicon carbide which act as insulation between different components within the converter to prevent heat transfer between them.
Additionally, some converters may also contain other elements such as iron oxide which helps reduce emissions further by trapping particles before they can escape out of the exhaust system. To learn more, check out our guide on what does a catalytic converter do and what do catalytic converters do.
Common Problems with Catalytic Converters and How to Fix Them
The catalytic converter is an important part of a vehicle’s exhaust system. It helps to reduce the number of harmful emissions released into the atmosphere. Unfortunately, catalytic converters can sometimes malfunction, leading to a variety of problems. Here are some common issues and how to fix them.
- One common problem with catalytic converters is clogging due to the buildup of carbon deposits or other debris in the exhaust system. This can cause reduced engine performance and increased fuel consumption as well as increased emissions levels. To fix this issue, it is necessary to clean out the exhaust system and replace any damaged parts such as oxygen sensors or spark plugs that may be contributing to the problem. So, make sure you’re on the lookout for the symptoms of a clogged catalytic converter.
- Another issue that can occur with catalytic converters is overheating due to a lack of airflow through the converter itself or from an obstruction in the exhaust pipe downstream from it. This can cause damage to both the converter and other components in your vehicle’s exhaust system, so it’s important to address this issue quickly by removing any obstructions or replacing any damaged parts such as mufflers or resonators that may be causing restricted airflow through your vehicle’s exhaust system.
- Finally, another common problem with catalytic converters is corrosion caused by exposure to moisture over time which can lead to cracks in its housing and eventual failure of its internal components. To prevent this from happening, it’s important for drivers regularly inspect their vehicles for signs of corrosion on their catalytic converters and replace them if necessary before they become too damaged for repair.
In conclusion, there are several common problems associated with catalytic converters that drivers should be aware of to keep their vehicles running smoothly while also reducing emissions levels released into our environment. By following these tips on how best to address these issues when they arise, you will help ensure your vehicle remains safe and reliable for years to come.
Understanding the Different Types of Catalytic Converters Available on the Market Today
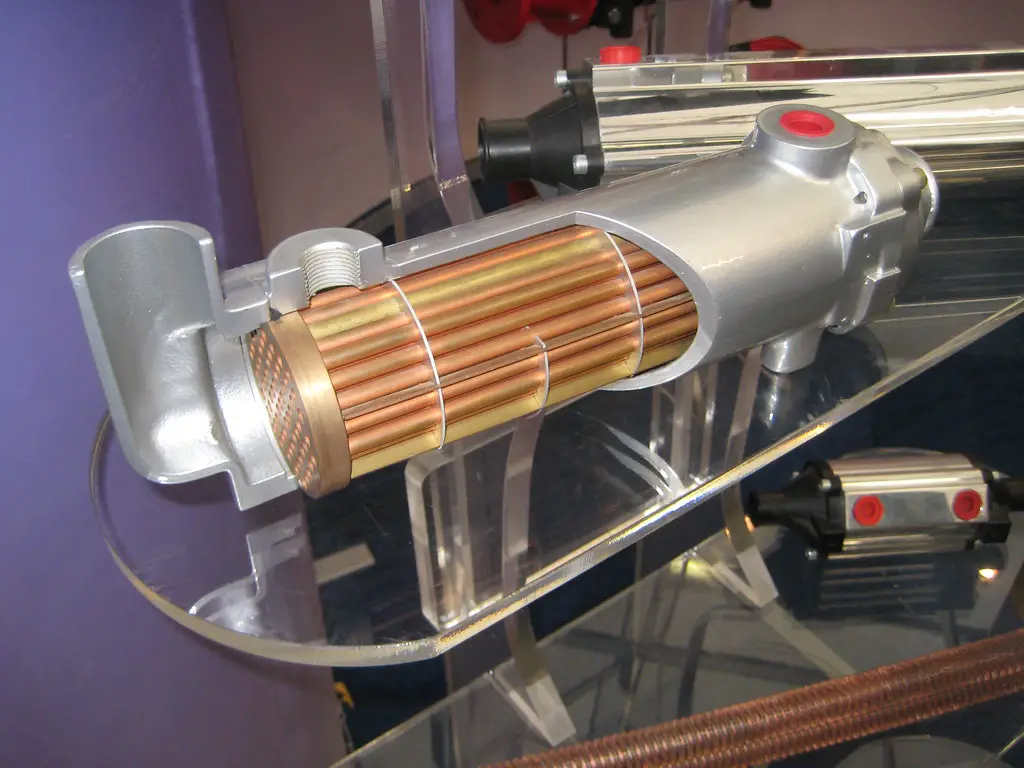
“Catalytic Converter” by Hiddenpower is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 2.0
Catalytic converters are an essential component of modern vehicles, as they help reduce the number of harmful emissions released into the atmosphere. There are several different types of catalytic converters available on the market today, each with its own unique features and benefits. In this article, we will discuss the various types of catalytic converters and their advantages.
- The most common type of catalytic converter is a three-way converter. This type uses a combination of platinum, palladium, and rhodium to convert carbon monoxide (CO) into carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrocarbons (HC) into water vapor (H2O), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into nitrogen gas (N2). Three-way converters are highly efficient at reducing emissions from gasoline engines but can be less effective when used with diesel engines.
- Another type of catalytic converter is a two-way converter. This type uses only platinum and palladium to convert CO into CO2 and HCs into H2O but does not reduce NOx levels as effectively as three-way converters do. Two-way converters are typically used in older vehicles that have lower emission standards or in diesel engines where NOx reduction is not required by law.
- A third type of catalytic converter is a diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC). DOCs use precious metals such as platinum or palladium to oxidize unburned hydrocarbons in diesel exhaust gases before they enter the atmosphere. DOCs can be very effective at reducing HC emissions from diesel engines but may not be able to reduce NOx levels sufficiently for some applications where stricter emission standards apply.
- Finally, there are also hybrid catalysts that combine two or more different types of catalyst materials together to achieve better overall performance than any single material could provide on its own. Hybrid catalysts can be particularly useful for applications where both high efficiency and low cost are desired simultaneously since they offer both benefits without sacrificing one for the other like traditional single-material solutions often do.
In conclusion, there are several different types of catalytic converters available on the market today that offer varying levels of performance depending on their application requirements and budget constraints. It is important for vehicle owners to understand these differences so that they can make an informed decision when selecting a new catalyst system for their vehicle’s exhaust system.
The Role of Oxygen Sensors in Regulating Emissions from a Vehicle with a Catalytic Converter Installed
The role of oxygen sensors in regulating emissions from a vehicle with a catalytic converter installed is essential for maintaining clean air. Oxygen sensors are used to measure the amount of oxygen present in the exhaust gases emitted by an engine.
This information is then used to adjust the fuel-air mixture, which helps reduce harmful emissions such as carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons. When a catalytic converter is installed on a vehicle, it works together with the oxygen sensor to further reduce emissions.
The catalytic converter uses precious metals such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium to convert harmful pollutants into less toxic substances before they are released into the atmosphere. Also, fun fact, go check out our write-up on the catalytic converter precious metal market prices.
The oxygen sensor monitors how much unburned fuel is present in the exhaust gases and adjusts the air-fuel mixture accordingly so that it can be efficiently converted by the catalytic converter. In order for this system to work properly, it must be calibrated correctly so that it can accurately measure and adjust air-fuel ratios according to engine load conditions.
If this calibration process is not done correctly or if there are any faults in either component (oxygen sensor or catalytic converter), then emissions will not be reduced effectively and may even increase due to incomplete combustion of fuel inside the engine cylinders.
Overall, oxygen sensors play an important role in regulating emissions from vehicles with a catalytic converter installed by monitoring air-fuel ratios and adjusting them accordingly so that they can be efficiently converted by the catalyst into less toxic substances before being released into our atmosphere (once you’ve understood what does a catalytic converter look like).
Comparing OEM and Aftermarket Options for Replacing Your Vehicle’s Existing Catalytic Converter
When it comes to replacing your vehicle’s existing catalytic converter, you have two main options: OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) and aftermarket. Both of these options offer advantages and disadvantages that should be considered before making a decision.
- OEM catalytic converters are designed specifically for the make and model of your vehicle, so they will fit perfectly with no modifications required. They also come with a manufacturer’s warranty, which can provide peace of mind in case something goes wrong. However, OEM converters tend to be more expensive than aftermarket ones due to their higher-quality materials and construction.
- Aftermarket catalytic converters are usually less expensive than OEM ones but may require some modifications to fit properly on your vehicle. Additionally, they often lack the same level of quality as an OEM converter and may not last as long or perform as well over time. On the other hand, aftermarket converters can provide a cost-effective solution if you are looking for a quick fix or don’t want to spend too much money on repairs.
Ultimately, when deciding between an OEM or aftermarket catalytic converter replacement for your vehicle (not to mention, what does a catalytic converter look like) it is important to consider both the advantages and disadvantages of each option before making a decision that best suits your needs and budget.
Properly Maintaining Your Vehicle’s Existing or Newly Installed Catalytic Converter
Properly maintaining your vehicle’s existing or newly installed catalytic converter is essential for ensuring that it continues to function properly. To ensure the longevity of your catalytic converter, there are several maintenance steps you should take.
- First, make sure to keep up with regular oil changes and tune-ups as recommended by the manufacturer. This will help prevent any build-up of dirt or debris in the exhaust system which can clog the catalytic converter and reduce its efficiency.
- Second, check your spark plugs regularly and replace them if necessary. Faulty spark plugs can cause misfires which can damage the catalytic converter over time.
- Third, inspect your exhaust system for any signs of corrosion or damage on a regular basis and repair any issues promptly to avoid further damage to the catalytic converter.
- Finally, use only high-quality fuel when filling up your vehicle as low-quality fuel can contain contaminants that may clog up the catalyst material inside the converter and reduce its efficiency over time.
By following these simple maintenance steps you will be able to ensure that your vehicle’s existing or newly installed catalytic converter remains in good working condition for many years to come (and make sure that what does a catalytic converter look like is in good condition inside).
Exploring the Latest Innovations in Automotive Technology
The automotive industry is constantly innovating to improve the performance of cars and reduce their environmental impact. One of the latest developments in this area is the use of advanced ceramic-based substrates for catalysts.
These substrates offer improved performance from your car’s catalyst, allowing it to more effectively convert harmful pollutants into less harmful substances. Catalysts are an essential component of a car’s exhaust system, as they help to reduce emissions by converting pollutants into less harmful substances before they are released into the atmosphere.
Traditionally, catalysts have been made from metals such as platinum or palladium, but these materials can be expensive and difficult to source in large quantities. Advanced ceramic-based substrates offer a cost-effective alternative that can be produced in large quantities with consistent quality control standards.
Ceramic-based substrates are composed of porous materials that provide an ideal surface for chemical reactions to take place on. This allows them to more effectively convert pollutants than traditional metal catalysts, resulting in improved performance from your car’s catalyst system and reduced emissions levels overall.
Additionally, ceramic-based substrates are highly durable and resistant to corrosion or damage caused by extreme temperatures or vibrations, making them ideal for long-term use in automotive applications.
In addition to their improved performance capabilities compared with traditional metal catalysts, advanced ceramic-based substrates also offer other benefits such as increased fuel efficiency due to reduced back pressure on the engine caused by their lightweight construction; increased durability due to their resistance against corrosion; and lower production costs due to their ability to be mass produced with consistent quality control standards.
Overall, advanced ceramic-based substrate technology offers significant improvements over traditional metal catalysts when it comes to improving your car’s performance while reducing its environmental impact at the same time. By investing in this technology now you can ensure that your vehicle will remain up-to-date with current emission regulations while also enjoying improved fuel efficiency and durability over time.

