- How Does a Catalytic Converter Work?
- Benefits of Installing a Catalytic Converter
- Common Problems with Catalytic Converters
- How to Diagnose a Bad Catalytic Converter
- Different Types of Catalytic Converters
- How to Choose the Right Catalytic Converter
- Cost of Replacing a Faulty Catalytic Converter
- Laws Surrounding Tailpipe Emissions
- Maintaining Your Vehicle’s Performance
- Repairing Your Car’s Catalyst Converter
What is a Catalytic Converter and How Does it Work?
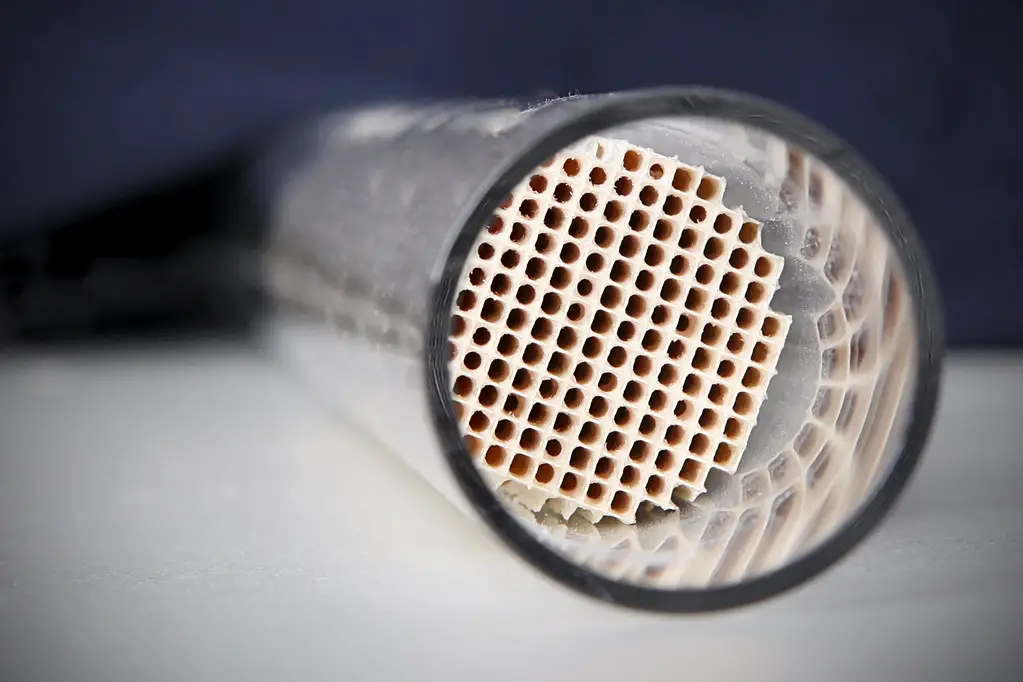
A catalytic converter is an emissions control device that is fitted to the exhaust system of a vehicle. It works by converting harmful pollutants in the exhaust gases into less harmful substances before they are released into the atmosphere.
The catalytic converter does this by using a catalyst, usually platinum or palladium, to chemically convert the pollutants into carbon dioxide and water vapor. The catalytic converter works by passing exhaust gases through a honeycomb-like structure coated with precious metals such as platinum and palladium.
These metals act as a catalyst, which means they speed up chemical reactions without being consumed themselves. You can learn more about these precious metals in our explainer on which catalytic converters have the most rhodium, as well as how much platinum is in a catalytic converter.
As the exhaust gases pass through this structure, they come into contact with these metals and undergo chemical reactions that convert them from harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and hydrocarbons (HC) into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O). This process helps reduce air pollution caused by vehicle emissions.
In addition to reducing air pollution, catalytic converters also help improve fuel efficiency by allowing engines to run more efficiently at lower temperatures. This is because when an engine runs at higher temperatures it produces more NOx which can be damaging to both human health and the environment if not properly controlled.
By controlling these emissions with a catalytic converter, engines can run more efficiently while still producing fewer pollutants than before. If you’re thinking about scrapping your catalytic converter, also check out our guide on the catalytic converter precious metal scrap prices.
The Benefits of Installing a Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter is an important component of a vehicle’s exhaust system. It helps reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere by converting them into less toxic substances. Installing a catalytic converter can provide numerous benefits, both to the environment and to your vehicle.
- One of the primary advantages of installing a catalytic converter is that it helps reduce air pollution. The device works by converting carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxides into harmless gases such as carbon dioxide and water vapor. This process helps keep our air clean and free from dangerous pollutants that can cause health problems for humans and animals alike.
- In addition to reducing air pollution, installing a catalytic converter can also improve your vehicle’s performance. The device helps increase fuel efficiency by allowing more oxygen to enter the engine’s combustion chamber, which in turn increases power output while decreasing fuel consumption. This means you will be able to get more miles out of each tank of gas while also reducing emissions from your car or truck.
- Finally, installing a catalytic converter may help you save money in the long run as well. Many states require vehicles to pass an emissions test before they are allowed on public roads; if your car or truck fails this test due to high levels of pollutants in its exhaust system, you may be required to pay for costly repairs or even replace parts such as the catalytic converter before being allowed back on the road again. By investing in one now, you can avoid these potential costs down the line while also helping protect our environment at the same time.
Common Problems with Catalytic Converters
The catalytic converter is an important part of a vehicle’s exhaust system, as it helps to reduce the number of harmful emissions released into the atmosphere. Unfortunately, these components can be prone to problems and failure. Common issues with catalytic converters include clogging, overheating, and damage due to fuel contamination.
- Clogging is one of the most common problems associated with catalytic converters. This occurs when particles such as soot or ash build up inside the converter and block its flow. This can cause a decrease in engine performance and an increase in emissions levels. To prevent this from happening, it is important to regularly maintain your vehicle’s exhaust system by replacing air filters and spark plugs on a regular basis. So, be wary of the symptoms of a clogged catalytic converter.
- Overheating is another issue that can affect catalytic converters. When the component gets too hot due to excessive use or lack of maintenance, it can cause damage to its internal components which will lead to decreased performance or even complete failure of the unit. To avoid this problem, make sure you are not overworking your engine by driving at high speeds for extended periods of time or carrying heavy loads in your vehicle for long distances without taking breaks in between trips. Additionally, ensure that you are regularly checking your oil levels and replacing any worn-out parts as needed so that your engine does not become too hot while running. You can confirm this with a catalytic converter temperature test.
- Finally, fuel contamination can also be a problem for catalytic converters if there are impurities present in the gasoline being used by your vehicle’s engine such as dirt or water droplets which could potentially damage its internal components leading to decreased performance or complete failure of the unit altogether. To prevent this from happening make sure you only use clean gasoline when filling up your tank and check for any signs of contamination before doing so if possible (elevated levels of sediment). Additionally, have any necessary repairs done immediately if you notice any changes in how well your car runs after refueling it with contaminated gasoline so that further damage does not occur over time due to prolonged exposure.
How to Diagnose a Faulty Catalytic Converter
Diagnosing a faulty catalytic converter can be a difficult task, as the symptoms of a failing converter can be similar to those of other engine problems. However, there are certain signs that may indicate that the catalytic converter is not functioning properly.
The first sign of a faulty catalytic converter is an illuminated check engine light on the dashboard. This indicates that there is an issue with one or more components in the vehicle’s exhaust system, and it could be caused by a malfunctioning catalytic converter.
Another symptom of a failing catalytic converter is reduced fuel efficiency and power output from the engine. This occurs because when the catalyst inside the unit becomes clogged or damaged, it restricts exhaust flow and reduces performance.
In some cases, you may also notice an unusual smell coming from your vehicle’s exhaust system when accelerating or idling at low speeds. This smell could indicate that your catalytic converter has overheated due to excessive backpressure in the exhaust system caused by clogging or damage to its internal components.
Finally, if you hear rattling noises coming from underneath your car while driving at low speeds, this could also indicate that your catalytic converter needs to be replaced as it may have become loose due to damage or corrosion over time. So, do take note of the signs of a bad catalytic converter.
If any of these symptoms are present in your vehicle then it is recommended that you take it for professional diagnosis and repair as soon as possible to avoid further damage being done to other parts of your car’s exhaust system such as oxygen sensors and mufflers which can lead to costly repairs down the line if left unchecked for too long.
The Different Types of Catalytic Converters Available
Catalytic converters are an important part of a vehicle’s exhaust system. They help reduce the number of harmful pollutants released into the atmosphere by converting them into less harmful substances. There are several different types of catalytic converters available, each designed to meet specific needs and requirements.
- The most common type is the three-way catalytic converter, which is used in most gasoline-powered vehicles. This type of converter uses a combination of platinum, palladium, and rhodium to convert carbon monoxide (CO) into carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrocarbons (HC) into water vapor (H2O), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into nitrogen gas (N2).
- Another type is the diesel oxidation catalyst, which is used in diesel engines. This converter uses a combination of platinum and palladium to convert CO and HC into CO2 and H2O respectively. It also helps reduce NOx emissions by oxidizing them with oxygen from the air intake system.
- The selective catalytic reduction (SCR) converter is another option for diesel engines that helps reduce NOx emissions even further by injecting urea or ammonia solution directly into the exhaust stream before it enters the SCR catalyst chamber where it reacts with NOx molecules to form harmless nitrogen gas and water vapor.
- Finally, there are also hybrid catalytic converters available that combine two or more technologies such as three-way catalysis with SCR technology for maximum efficiency in reducing emissions from both gasoline-powered vehicles as well as diesel engines.
Overall, there are many different types of catalytic converters available in today’s market depending on your vehicle’s needs and requirements for reducing emissions levels while still providing optimal performance levels at all times.
How to Choose the Right Catalytic Converter for Your Vehicle
“Catalytic Converter” by Hiddenpower is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 2.0
When it comes to replacing a catalytic converter, it is important to choose the right one for your vehicle. The wrong converter can cause damage to your engine and reduce its performance. Here are some tips on how to choose the right catalytic converter for your vehicle.
- First, you need to determine what type of catalytic converter is compatible with your vehicle. Most vehicles use either a two-way or three-way catalytic converter, so you will need to know which type is required for your car or truck. You can find this information in the owner’s manual or by contacting a local auto parts store.
- Second, you should consider the size of the catalytic converter that is needed for your vehicle. The size of the catalyst will depend on several factors such as engine displacement and exhaust system design. It is important that you get an exact match to ensure optimal performance from your engine and exhaust system.
- Third, make sure that you purchase a high-quality product from a reputable manufacturer or supplier. Low-quality converters may not last as long as higher-quality ones and could potentially cause damage if they fail prematurely due to poor construction or materials used in their manufacture.
- Finally, be sure that any replacement parts are covered by a warranty before making any purchases so that if something goes wrong with them during installation or operation they can be replaced without additional cost to you down the road.
By following these tips when selecting a new catalytic converter for your vehicle, you can ensure that it will provide optimal performance while also protecting against potential damage caused by low-quality components and materials used in its manufacture.
The Cost of Replacing a Faulty or Damaged Catalytic Converter
The cost of replacing a faulty or damaged catalytic converter can vary significantly depending on the make and model of your vehicle. Generally, the cost of a replacement catalytic converter ranges from $400 to $2,000. The price is largely determined by the type of car you drive and the complexity of installation.
In addition to the cost of purchasing a new catalytic converter, there may be additional labor costs associated with its installation. Depending on your vehicle’s make and model, it may require special tools or expertise to properly install a new catalytic converter. This could add an additional $100-$500 in labor costs to your total bill.
It is important to note that some states have laws requiring that only certified technicians install aftermarket parts such as catalytic converters. If this is applicable in your state, you will need to factor in any additional fees associated with having a certified technician perform the work for you.
Finally, if you are considering replacing your own faulty or damaged catalytic converter, it is important that you understand all safety precautions before attempting any repairs yourself as improper installation can lead to further damage and costly repairs down the line.
Understanding the Laws Surrounding Emissions and the Use of a Catalytic Converter
The laws surrounding emissions and the use of a catalytic converter are complex and important to understand. A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that reduces toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction.
It is an essential component of any vehicle’s emissions system, as it helps reduce the number of harmful gases released into the atmosphere. In order to comply with federal regulations, all vehicles must be equipped with a properly functioning catalytic converter.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets standards for vehicle emissions, which are enforced through state and local laws. These standards require that vehicles meet certain levels of air pollution control to be legally operated on public roads.
The EPA also requires that all new cars have a three-way catalyst installed in their exhaust systems, which consists of two oxygen sensors and one catalyst element. This three-way catalyst helps reduce hydrocarbon (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions from gasoline engines by converting them into harmless water vapor and nitrogen gas before they can enter the atmosphere.
In addition to meeting EPA requirements, many states have adopted their own regulations regarding vehicle emissions testing programs or smog checks for older vehicles or those registered in certain areas where air quality is poor due to high levels of pollution from motor vehicles.
These tests measure the amount of HC, CO, NOx, particulate matter (PM), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and lead compounds (PbC) present in the exhaust stream coming out of your car’s tailpipe at idle speed or during acceleration tests performed on dynamometers or other approved devices used for this purpose.
If your car fails these tests you may need to replace your existing catalytic converter with one that meets current EPA standards before you can pass inspection again. It is important for drivers to understand both federal regulations as well as any applicable state laws when it comes to operating their vehicles safely while also protecting our environment from harmful pollutants released by motor vehicles.
Tips for Maintaining Your Vehicle’s Performance with a Properly Functioning Catalytic Converter
1. Ensure your vehicle is running on clean fuel. Dirty fuel can cause the catalytic converter to become clogged, reducing its efficiency and performance.
2. Regularly check your vehicle’s air filter and replace it when necessary. A dirty air filter can reduce the oxygen supply to the catalytic converter, leading to a decrease in performance.
3. Have your engine tuned up regularly by a qualified mechanic or technician to ensure that all components are functioning properly and that there are no issues with the exhaust system or catalytic converter itself.
4. Make sure you use only high-quality motor oil in your vehicle as this will help keep the engine clean and free of debris which could potentially damage the catalytic converter over time if left unchecked.
5. Avoid using leaded gasoline as this can cause deposits to build up inside of the catalytic converter, reducing its efficiency and performance over time due to clogging or blockage of exhaust gases passing through it from the engine cylinders into the atmosphere outside of your car’s tailpipe system.
6. Check for any leaks in your exhaust system as these can also reduce oxygen flow into the catalytic converter, leading to decreased performance levels.
7. If you notice any strange noises coming from under your hood such as rattling or knocking sounds, have them checked out immediately by a qualified mechanic or technician who specializes in automotive repair services so they can diagnose any potential problems with your car’s exhaust system before they become more serious issues down the road.
Exploring Alternative Solutions to Replacing or Repairing Your Car’s Existing Catalyst Converter
The catalyst converter is an essential component of a car’s exhaust system, as it helps to reduce the number of harmful emissions released into the atmosphere. Unfortunately, these components can become damaged or worn out over time, leading to costly repairs or replacements.
Fortunately, there are some alternative solutions that may be able to help you avoid having to replace or repair your existing catalyst converter.
- One option is to install a catalytic converter bypass pipe. This device works by allowing exhaust gases to bypass the converter and flow directly out of the tailpipe without being filtered through the converter first. While this solution does not provide any environmental benefits, it can be a cost-effective way of avoiding expensive repairs or replacements for those who do not need their vehicle’s emissions levels reduced for legal reasons.
- Another option is to install an aftermarket catalytic converter replacement kit. These kits typically include all necessary components such as oxygen sensors and gaskets needed for installation and are designed specifically for certain makes and models of vehicles. They are usually much less expensive than purchasing a new factory-installed catalytic converter but may not offer as much protection against harmful emissions as an OEM part would provide.
- Finally, if your existing catalytic converter has become clogged with debris or other contaminants, you may be able to clean it rather than replace it entirely. This process involves using specialized cleaning agents that dissolve deposits to restore proper functioning without damaging any internal components in the process. However, this method should only be attempted by experienced mechanics due to its complexity and potential risks involved with improper cleaning techniques being used on sensitive parts like converters.
In conclusion, while replacing or repairing your car’s existing catalyst converter can often be necessary in order to maintain optimal performance levels and reduce harmful emissions output from your vehicle; there are some alternative solutions available that could potentially help you avoid such costs altogether depending on your specific needs and budget constraints at hand.


